

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
المؤلف:
John McMurry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 303
28-5-2017
2755
Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
We’ve pointed out on several occasions that some of the reactions discussed in this and earlier chapters are either oxidations or reductions. An organic oxidation results in a loss of electron density by carbon, caused either by bond formation between carbon and a more electronegative atom (usually O, N, or a halogen) or by bond-breaking between carbon and a less electronegative atom (usually H). Conversely, an organic reduction results in a gain of electron density by carbon, caused either by bond formationbetween carbon and a less electronegative atom or by bond-breaking between carbon and a more electronegative atom.

Based on these definitions, the chlorination reaction of methane to yield chloromethane is an oxidation because a C - H bond is broken and a C - Cl bond is formed. The conversion of an alkyl chloride to an alkane via aG rignard reagent followed by protonation is a reduction, however, because a C - Cl bond is broken and a C - H bond is formed.

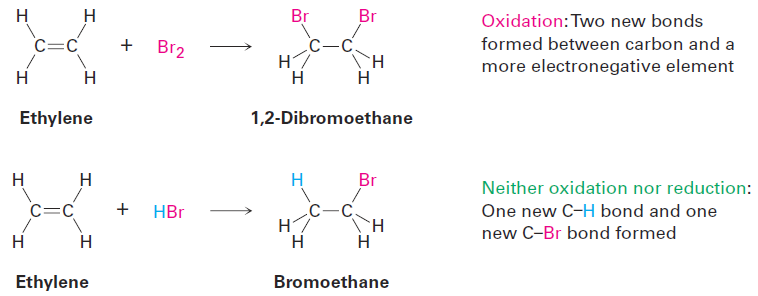
As other examples, the reaction of an alkene with Br2 to yield a 1,2-dibromide is an oxidation because two C - Br bonds are formed, but the reaction of an alkene with HBr to yield an alkyl bromide is neither an oxidation nor a reduction because both a C - H and a C - Br bond are formed.
A list of compounds of increasing oxidation level is shown in Figure 1.1. Alkanes are at the lowest oxidation level because they have the maximum possible number of C - H bonds per carbon, and CO2 is at the highest levelbecause it has the maximum possible number of C - O bonds per carbon. Any reaction that converts a compound from a lower level to a higher level is an oxidation, any reaction that converts a compound from a higher level to a lower level is a reduction, and any reaction that doesn’t change the level is neither an oxidation nor a reduction.

Figure 1.1 Oxidation levels of some common types of compounds.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















