


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 11-10-2019
Date: 28-10-2020
Date: 24-9-2020
|
A Comparison Between Biological Reactions and Laboratory Reactions
Beginning in the next chapter, we’ll be seeing a lot of reactions, some that are important in laboratory chemistry yet don’t occur in nature and others that have counterparts in biological pathways. In comparing laboratory reactions with biological reactions, several differences are apparent. For one, laboratory reactions are usually carried out in an organic solvent such as diethyl ether or dichloromethane to dissolve the reactants and bring them into contact, whereas biological reactions occur in the aqueous medium within cells. For another, laboratory reactions often take place over a wide range of temperatures without catalysts, while biological reactions take place at the temperature of the organism and are catalyzed by enzymes.
The active site is lined by acidic or basic groups as needed for catalysis and has precisely the right shape to bind and hold a substrate molecule in the orientation necessary for reaction. Figure 1.1 shows a molecular model of hexokinase, along with an X-ray crystal structure of the glucose substrate and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) bound in the active site. Hexokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the initial step of glucose metabolism—the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to glucose, giving glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.
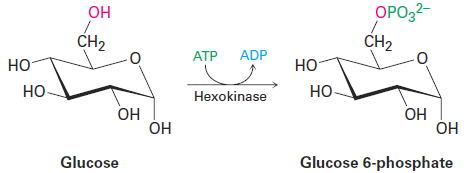
Note how the hexokinase-catalyzed phosphorylation reaction of glucose is written. It’s common when writing biological equations to show only the structures of the primary reactant and product, while abbreviating the structures of various biological “reagents” and by-products such as ATP and ADP. A curved arrow intersecting the straight reaction arrow indicates that ATP is also a reactant and ADP also a product.

Figure 1.1 Models of hexokinase in space-filling and wire-frame formats, showing the cleft that contains the active site where substrate binding and reaction catalysis occur. At the bottom is an X-ray crystal structure of the enzyme active site, showing the positions of both glucose and ADP as well as a lysine amino acid that acts as a base to deprotonate glucose.
Yet another difference between laboratory and biological reactions is that laboratory reactions are often done using relatively small, simple reagents such as Br2, HCl, NaBH4, CrO3, and so forth, while biological reactions usually involve relatively complex “reagents” called coenzymes. In the hexokinasecatalyzed phosphorylation of glucose just shown, ATP is the coenzyme. As another example, compare the H2 molecule, a laboratory reagent that adds to a carbon–carbon double bond to yield an alkane, with the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) molecule, a coenzyme that effects an analogous addition of hydrogen to a double bond in many biological pathways. Of all the atoms in the coenzyme, only the one hydrogen atom shown in red is transferred to the double-bond substrate.

Don’t be intimidated by the size of the ATP or NADH molecule; most of the structure is there to provide an overall shape for binding to the enzyme and to provide appropriate solubility behavior. When looking at biological molecules, focus on the small part of the molecule where the chemical change takes place.
One final difference between laboratory and biological reactions is in their specificity. A catalyst might be used in the laboratory to catalyze the reaction of thousands of different substances, but an enzyme, because it can only bind a specific substrate molecule having a specific shape, will usually catalyze only a specific reaction. It’s this exquisite specificity that makes biological chemistry so remarkable and that makes life possible. Table 1.1 summarizes some of the differences between laboratory and biological reactions.
Table 1.1 A Comparison of Typical Laboratory and Biological Reactions




|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|