

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Fusion Nomenclature System Of Heterocyclic ompounds
المؤلف:
R. R. Gupta, M. Kumar, V. Gupta
المصدر:
Heterocyclic Chemistry I
الجزء والصفحة:
p 19
22-12-2016
9334
Fusion Nomenclature System Of Heterocyclic ompounds
The systematic names of the fused heterocycles are given by this nomenclature system. The fused heterocyclic system is considered to be constructed by the combination of two or more cyclic structural units (components). The cyclic structural units contain maximum number of non-cumulative double bonds and are fused in such a way that each structural unit (component) has one bond common with other. The names of the structural units can be trivial or systematic. The fused heterocyclic system are named according to the following rules :
1. The fused heterocyclic system is dissected into its components in which one is base component and other(s) is attached component(s).
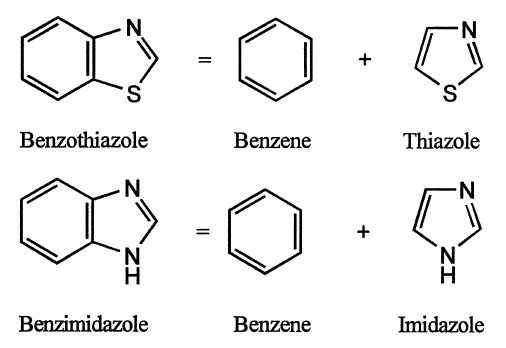
2. The components are given their recognized trivial names, if possible, which are selected from the Table of trivial names (Table below).
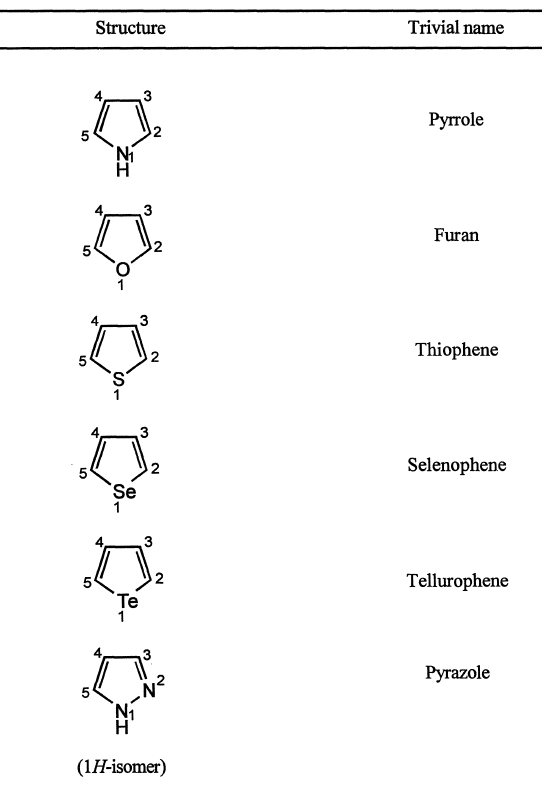

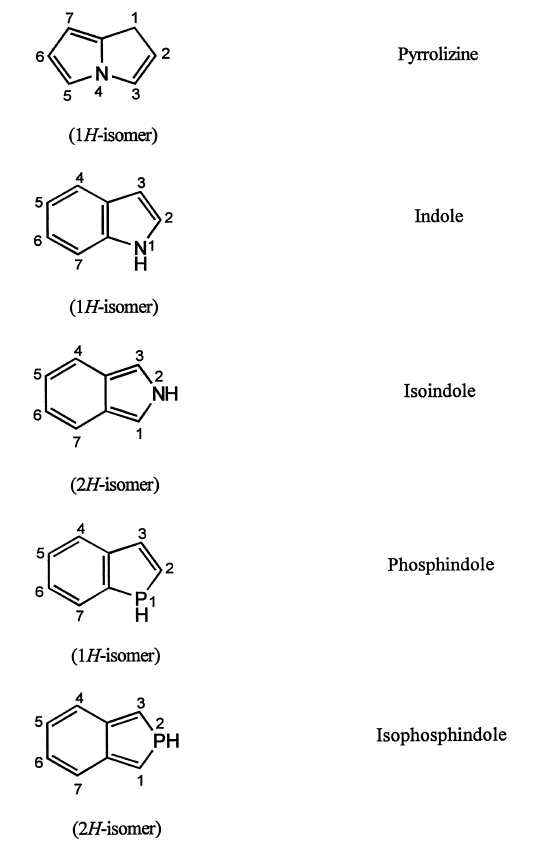
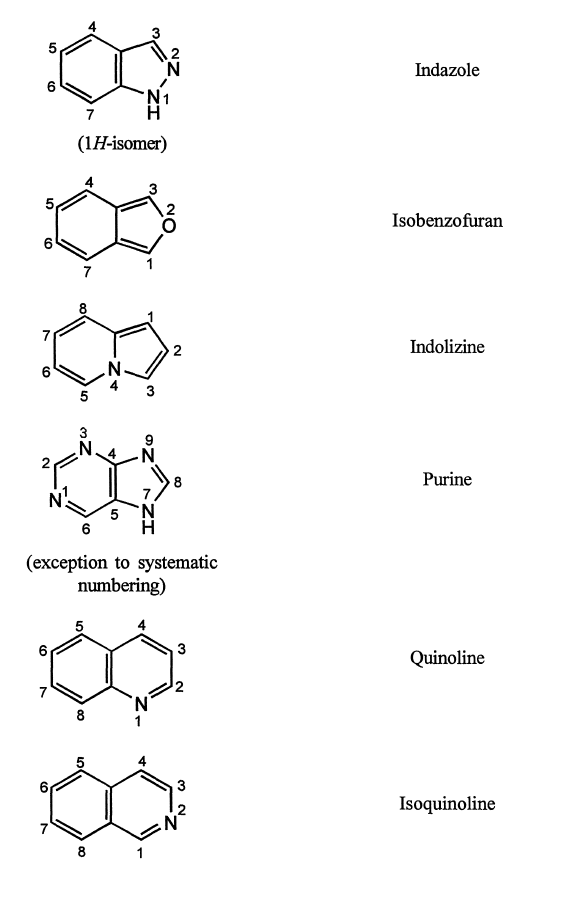
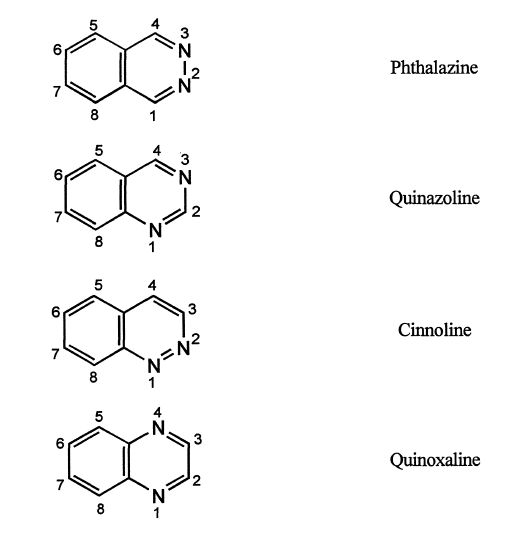
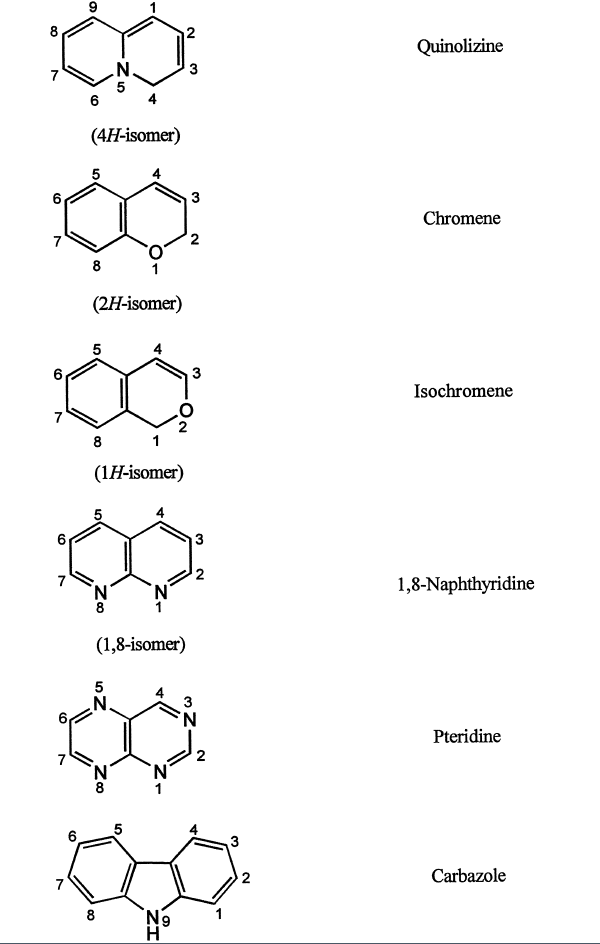
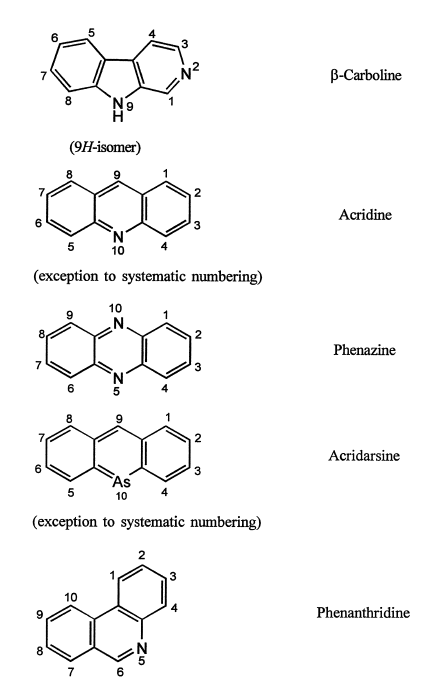
If mono cyclic component has no recognized trivial name, the systematic name is used.
3. Base component should be a heterocyclic system. If there is choice, the base component is determined by the order of preference.
Selection of Base Component:
(i) Nitrogen containing component : a nitrogen containing component is selected as the base component.

(ii) Component(s) with heteroatom(s) other than nitrogen: if nitrogen is absent in the heterocyclic ring(s), the ring with other heteroatom(s) is selected as the base component.

If both the components contain heteroatoms other than nitrogen, the component which contains heteroatom appearing highest (Table in below) is selected base component (component with heteroatom of highest group in periodic table and with heteroatom of higher atomic number if heteroatoms are of the same group).
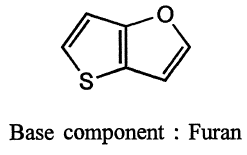
(iii) Component with greatest number of rings: a component with as many rings as possible is selected as the base component (bicyclic condensed systems or polycyclic systems with recognized trivial names).
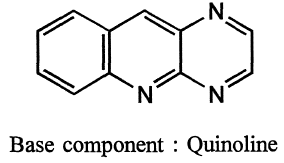
(iv) Rings of unequal size : if fused heterocyclic system contains rings of unequal size, the component with the largest size of the ring is selected as a base component.
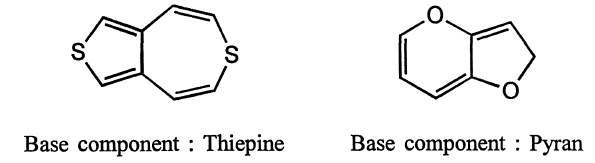
(v) Rings of equal size with different number ofheteroatoms : if the heterocyclic system containing rings of equal size with different number of heteroatoms, the ring with greater number of heteroatoms of any kind is considered as a base component.
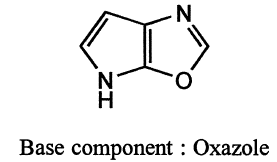
(vi) Rings of equal size with equal number of different heteroatoms : ifboth the components contain rings of same size with equal number of different heteroatoms, the component containing ring with greatest variety of heteroatoms is selected as a base component.
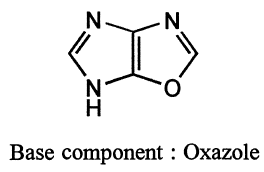
If two heteroatoms of the same group are present, the component containing the ring with heteroatoms appearing first in Table 1 is preferred as the base component.
Table 1.Prefixes for heteroatoms
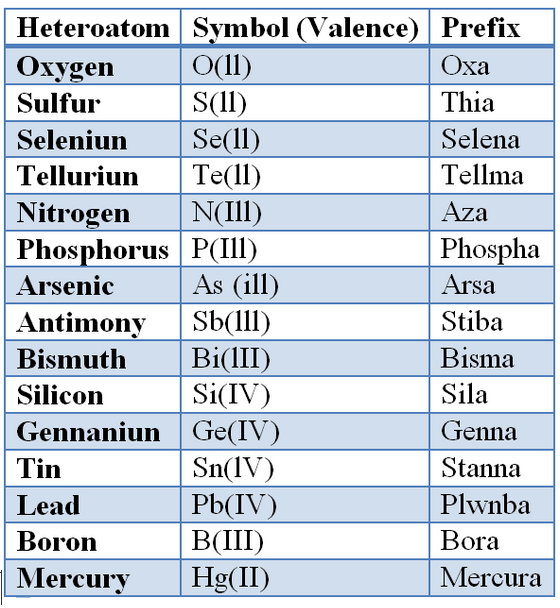
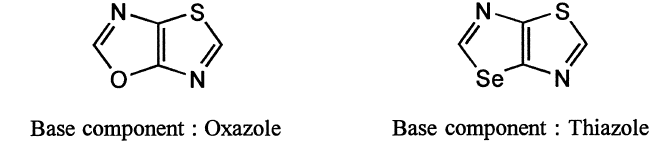
(vii) Rings of same size with same numbers and same kinds of heteroatoms : if the components contain rings of the same size with same numbers and same kinds of heteroatoms, the component containing ring with heteroatoms which have the lowest locant numbers is preferred as a base component.

4. The attached component (second component) is added as a prefix to thename of the base component. The prefix designating an attached component is formed by changing terminal 'e' of a trivial or HantzschWidman name of a component into 'o'. This 'o' is not dropped when followed by a vowel.
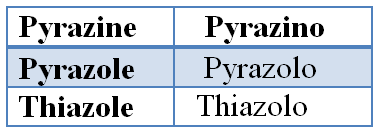
However, there are some exceptions to this rule. The prefixes for some common heterocycles used in the fused nomenclature are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Prefixes for some common heterocycles

5. The bonds of the base component are alphabetized with consecutive italic letters starting with 'a' for 1,2- bond, 'b' for 2,3-bond, 'c' for 3,4-bond 'd' for 4,5-bond and so on.
6. The atoms of ring system of second component (attached component) are numbered in the normal way; 1,2,3,4,5, etc., observing the principle of the lowest possible numbering.
7. The atoms common to both rings (side of fusion) are indicated by the appropriate letters and numbers and are enclosed in a square bracket and placed immediately after the prefix of the attached component. The numbers (positions of attachment) of the second component are placed in the sequence in which they are attached to the base component.
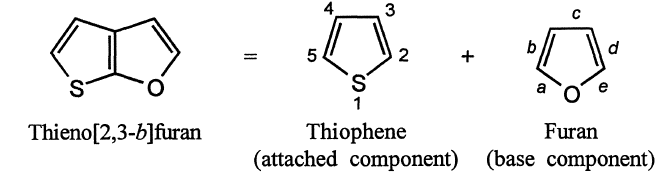
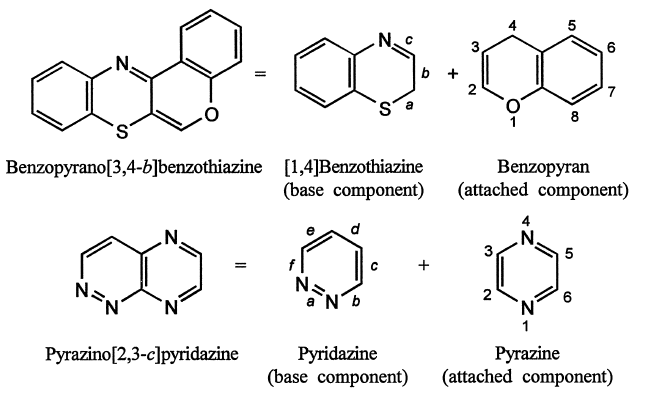
8. Common heteroatom : If a position of fusion is occupied by a heteroatom, both the components (ring systems) are considered to possess that heteroatom.
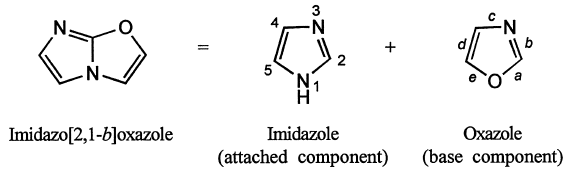
9. Numbering of fused heterocyclic system :
(i) Fused heterocyclic system is numbered independently of the combining components (base and attatched components). The numbering is started from the atom adjacent to the bridgehead position with the lowest possible locant(s) to the heteroatom(s). If there is choice, the heteroatom appearing highest in Table 1 is preferred.
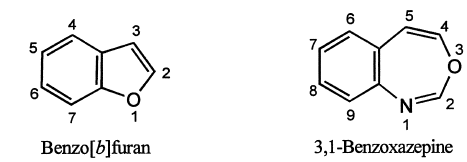
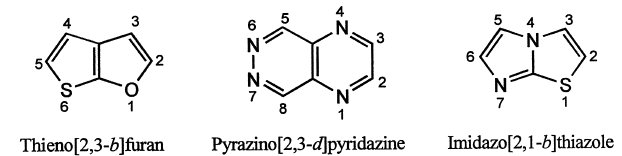
(ii) Carbon atom common to two rings is given the lowest possible position, but not numbered. However, the heteroatom at a position of fusion of two rings (common heteroatom) is numbered.

(iii) The position of a saturated atom is indicated by an italic hydrogen and is given the lowest possible number locant.
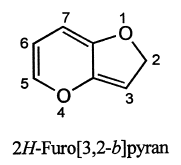
10. Benzofused heterocycles :
(i) If a benzene ring is fused to the heterocyclic ring, the compound is named by placing number(s) indicating position(s) of the heteroatom(s) before the prefix benzo- ( from benzene) followed by the name of the heterocyclic component.
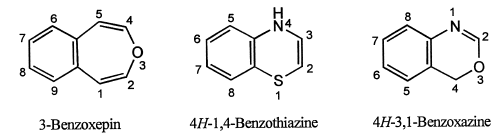
(ii) If two benzene rings are ortho-fused to a six-membered 1,4-diheteromonocyclic ring containing different heteroatoms, the heterocyclic system is named by adding the prefix 'pheno-' to the Hantzsch-Widman name of the heteromonocycle.
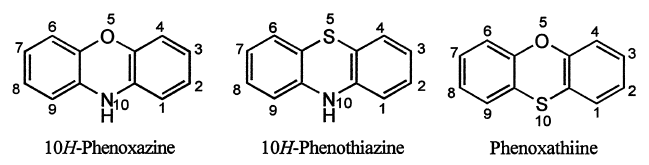
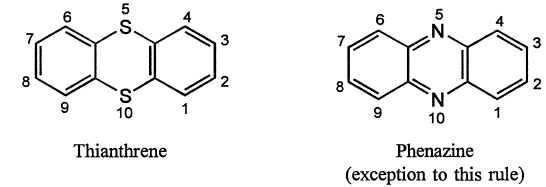
(iii.) However, the heterocyclic system in which two benzene rings are orthofused to a six-membered 1,4-diheteromonocycle containing the same heteroatoms are named by adding the replacement prefix for the heteroatom (Table 1) to the term '-anthrene' with elision of an 'a'.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















