
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
What Causes an Acceleration?
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
p 66
15-12-2016
2790
What Causes an Acceleration?
So far we have studied some things about acceleration but we never considered what causes things to accelerate. The answer is force. The gravitational force causes objects to fall (i.e. accelerate downwards). Friction force causes cars to slow down (decelerate), etc. Fundamental classical physics is all about finding the force. Once you know that you can get acceleration as we shall see. Once you have the acceleration, you can find velocity, displacement and time as we have studied previously.
Newton's First Law
A body remains in a state of rest, or uniform motion in a straight line, unless acted upon by a force.
Newton's Second Law
Newton's second law of motion is not something we can derive from other equations. Rather it is a fundamental postulate of physics. It was introduced by Isaac Newton to describe the cause of acceleration. The law is

Σ represents the sum (Σ) of all forces (
represents the sum (Σ) of all forces ( ) acting on a single body of mass m. The body then undergoes an acceleration given by
) acting on a single body of mass m. The body then undergoes an acceleration given by  One of the key activities in classical physics is to find all the forces Σ
One of the key activities in classical physics is to find all the forces Σ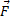 . Once you have them then you have the acceleration via
. Once you have them then you have the acceleration via  and once you have that you can get velocity, displacement and time. Now Newton's second law is a vector equation. Thus its actual meaning is given by 3 equations, namely
and once you have that you can get velocity, displacement and time. Now Newton's second law is a vector equation. Thus its actual meaning is given by 3 equations, namely

Once we have ΣFx, ΣFy, ΣFz we just divide by m to give the accelerations ax, ay, az. If they are constant, just plug them into the constant acceleration equations and solve for the other quantities you are interested in. One extra point is the units. The units of a are m/sec2. The units of m are kg and thus the units of F are kg m/sec2. This is given a special name called Newton (N). Thus

In the English system of units a Pound (lb) is a unit of force. The mass unit is called slug. The units of acceleration are foot/sec2. thus

Newton's Third Law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















