


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 12-11-2016
Date: 12-11-2016
Date: 2-10-2016
|
Kordylewski Clouds
By Kepler’s laws any object orbiting the Sun in an orbit smaller than Earth’s has a faster speed. So how can dust particles placed in solar orbit along the Earth-Sun radial line but closer to the Sun have the same speed as Earth?
Answer
Joseph L. Lagrange in the late 1700s calculated via Newton’s laws that there are five special positions for objects bound by any two-body system. Now called Lagrange points, positions L1, L2, and L3 are unstable, while L4 and L5 are stable. Several spacecraft have been placed at or near these Lagrange points, and there have been proposals for building space colonies at the L4 or L5 positions.
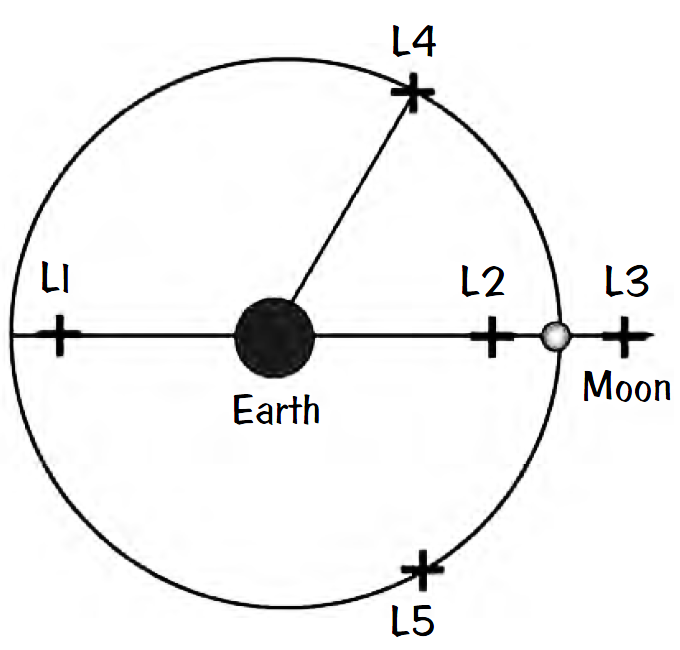
Applying Kepler’s third law for a particle of mass μ between Earth’s mass m and the Sun’s mass M orbiting with Earth’s period T, one obtains after several steps GMμ/(r–R)3 – Gmμ/(R2(r–R)) = GMμ/r3 where r is the Earth–Sun distance and R is the Earth–particle distance. The particle at L1 will be about 0.01 times the distance to the Sun. The L3 point on the night side of Earth can be calculated in the same way, replacing r–R with r+R. However, the other three points must be calculated with the gravitational attractions of the other planets included.
Similar calculations have been done for the five Lagrange points for the Earth-Moon system. Polish astronomer K. Kordylewski in 1961 reported the observation of dust clouds at the L5 point, but some observers have not seen them. Particles here may not remain long before being ejected, according to calculations.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|