
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Galaxy Rotation
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p111
10-11-2016
792
Galaxy Rotation
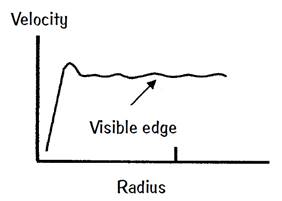
One of the great surprises in astronomy is the rotational behavior of galaxies that is, all the stars in the galactic disk revolve at roughly the same tangential speed! Two immediate conflicts with conventional physics arise: (1) If Newtonian gravitation and Kepler’s laws apply, they would dictate a decrease in star velocity with increasing radius from the galactic nucleus, like the planets of the Solar System do. (2) If the spiral arms of a spiral galaxy are to retain their integrity and persist for at least ten complete revolutions, as they have for the Milky Way, there must be something preventing them from wrapping numerous times. By assuming that Newton’s universal law of gravitation applies to these galactic problems, what general type of mass/energy distribution must be proposed to explain the rotational velocity curve? What further hypotheses might you propose? 219. Cosmic?
Answer
To retain a Newtonian gravitation explanation for the rotation properties of a galaxy, additional matter, called “dark matter,” in a halo surrounding the galaxy has been proposed, its mass being about 10 times the mass of the visible mass! Known particles such as electrons, protons, neutrinos and so on cannot be its major constituents; otherwise the particles in the halo would have been detected already. Some exotic form of matter/energy is required in this galactic halo. However, any type or types of possible “dark matter” in sufficient quantities has not yet been found.
An interesting proposal that does not require “dark matter” is called MOND, an acronym for modified Newtonian dynamics, which applies whenever the inward radial acceleration in the galaxy is below the value a0 = –1.1 × 10–10 m s–2, an incredibly small amount by Earth standards but a value that occurs in most galaxies. Essentially, MOND replaces the Newtonian acceleration gN by 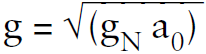 . All galaxies examined so far seem to obey the consequences of this ad hoc rule by using the galactic visible matter only, but its possible origin in terms of fundamental physics principles is being investigated still. The major problem for MOND has been its inability to accommodate the empirical results on the focusing of distant starlight by gravitational lensing.
. All galaxies examined so far seem to obey the consequences of this ad hoc rule by using the galactic visible matter only, but its possible origin in terms of fundamental physics principles is being investigated still. The major problem for MOND has been its inability to accommodate the empirical results on the focusing of distant starlight by gravitational lensing.
An even more exotic solution has been proposed to explain galaxy rotation without requiring “dark matter.” Briefly, the large-scale structure and behavior of the galaxy may result from the galaxy being in some quantization state. In modeling this type of theory, all the disk stars would be in the same quantization state independent of position radially and, by the virial theorem, must have the same tangential velocity V = GM2/(nJ), where M is the amount of visible mass, n is a small integer, and J is the total angular momentum of this visible mass of the galaxy. Substituting reasonable values for our Galaxy (the Milky Way), for example, one obtains a value near to the measured value of V = 220 km s–1. This theory predicts that the next quantization state would have exactly half the disk tangential velocity and, indeed, in 2003 a mass current of stars circulating the Galaxy just beyond the “edge of the easily visible disk” with a tangential velocity of 110 km s–1 was determined serendipitously from data collected by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS)! Whether this proposed large-scale quantization faithfully represents gravitational behavior in galaxies and in the universe remains to be fully examined.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















