

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Mitochondria
المؤلف:
AN INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOLOGY-1998
المصدر:
JAMES D. MAUSETH
الجزء والصفحة:
24-10-2016
2975
Mitochondria
Cells store energy as highly energetic but fairly unreactive compounds, such as sugars and starches; to utilize the energy, such compounds must be broken down and their energy used to synthesize new compounds that are both highly energetic and very reactive, the most common being adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Because these reactions involve high- energy, reactive compounds, they occur more safely within a discrete organelle than freely in the cytoplasm, where the intermediates might accidentally react with other cell components. Mitochondria (sing.: mitochondrion) are the organelles that carry out this cell respiration (Fig. 1).
Many steps of respiration are mediated by enzymes bound to mitochondrial membranes The enzymes are located adjacent to each other so that the product of one reaction (which becomes the reactant in the next reaction) is passed directly to the next enzyme; this controls the highly reactive intermediates (Fig. 2). Mitochondrial membranes are fielded, forming large sheets or tubes known as cristae (sing.: crista). This folding provides room for large numbers of enzymes.
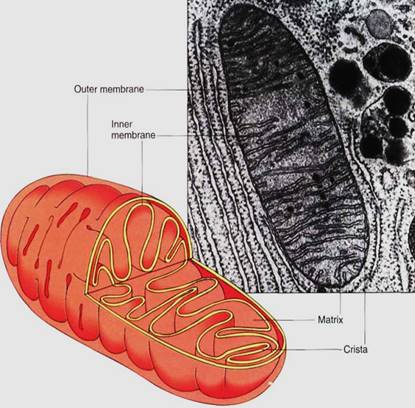
FIGURE 1: The inner mitochondrial membrane is folded into platelike cristae, giving it a large surface area; many respiratory enzymes are intrinsic proteins embedded in the crista membrane. The large surface area makes it possible to contain many copies of each enzyme, and more reactions can occur simultaneously.
Reactions that do not involve highly reactive intermediates take place in the liquid matrix between the cristae. Around this complex of cristae and matrix is a second membrane, the outer mitochondrial membrane, which probably just gives shape and a little rigidity to the mitochondrion. The outer membrane is rather freely permeable, but the inner mitochondrial membrane, which forms the cristae, is selectively permeable and has numerous pumps and channels.
Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes, both of which are different from those of the rest of the cell. Mitochondrial DNA is a circular molecule and lacks histones; the ribosomes are small and resemble those found in prokaryotes.
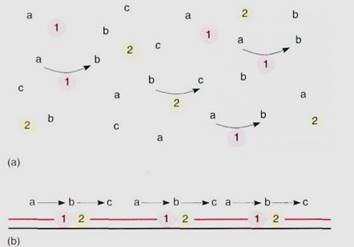
FIGURE 2: Many enzymes must work together. The product b of enzyme 1 is the reactant of enzyme 2. (a) If the enzymes are in solution, they may not be close together and b must diffuse at random until it encounters enzyme 2; in the meantime, it may accidentally react with something else. (b) If they are located side by side on a membrane, enzyme 1 can pass b directly to enzyme 2, not only speeding up the overall reaction but also eliminating the chance of accidental reactions.
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles; they can grow larger, either as the cell does or as the cell's need for respiration increases. They are often about 1 pm in diameter but up to 5 pm in length, and even much longer in some cases. Mitochondria can also divide into two, increasing the number of mitochondria per cell. Under rare conditions, the mitochondria in some species fuse together, forming a single giant mitochondrion in each cell. Mitochondria occupy between 1% and 25% of the cell volume; the higher values are similar to those for animal cells. Because of their ability to divide and fuse, the actual number of mitochondria per cell (usually in the range of 100 to 10,000) may not be as important as their volume.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم النبات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم النبات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















