
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Forces and Accelerations
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 44
13-10-2016
747
Forces and Accelerations
In Newtonian physics, an applied contact force acting on a rigid object will accelerate the object in the same direction as the applied force. Does this behavior hold for applied contact forces in relativity physics (STR)? For example, if an applied contact force pushes on the same rigid object in the direction perpendicular to the direction of motion, will the resulting acceleration be in the direction of the applied contact force?
Answer
No. In the STR, all contact forces will produce an acceleration in a direction not parallel to the applied force! For example, a rigid sphere is moving along the plus x-direction of an inertial reference frame. Now let an applied contact force act in the plus y-direction to increase the speed of the sphere in the y-direction. What happens to the speed in the x-direction? The x-component of the speed decreases the object slows down in its original direction, corresponding to a negative acceleration!
To understand why the object slows in the x-direction when the applied contact force is in the y-direction, we begin with the space-time interval: (interval)2 = c2 Δt2 – Δx2 – Δy2 – Δz2. For real objects traveling at speeds less than c, the time term is much larger than the spatial terms, and the interval is called the proper time τ. The linear momentum px in the x-direction in Newtonian physics is defined as px = m dx/dt (for an object that is not changing its mass, i.e., excluding objects such as a leaking bucket of water). The correct STR expression simply substitutes proper time τ for Newtonian time t so that px = m dx/dτ. For a low-velocity object, dτ ~ dt. But the actual relationship between τ and t depends on the magnitude of the object’s total velocity, a vector quantity, not just the speed component in the x-direction. Therefore, as the object speeds up in the y-direction, its speed in the x-direction must decrease to maintain a constant total velocity magnitude, otherwise its x-component of linear momentum would change, forbidden by the law of conservation of linear momentum. The pertinent relationship is dt/dτ = 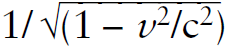 . Remember, the mass is fixed in value.
. Remember, the mass is fixed in value.
One could write down the relativistic momentum 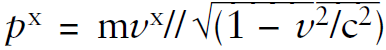 and argue that since m is constant, the component of velocity in the original direction must decrease to keep the momentum component constant.
and argue that since m is constant, the component of velocity in the original direction must decrease to keep the momentum component constant.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















