


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-8-2016
Date: 26-8-2016
Date: 2-8-2016
|
Powder of Dielectric Spheres
A powder composed of small spherical particles (with ε = 4 and of radius R = 100 nm) is dispersed in vacuum with a concentration of n = 1012 particles per cm3. Find the effective dielectric constant ε' of this medium. Explain why the apparent answer,

(where V = 4πR3/3 is the volume of one particle) is wrong.
Hint: Make use of the fact that nR3 << 1. Exploit the spherical symmetry of the particles.
SOLUTION
To find the effective dielectric constant, we must first find the polarization of the spherical particles. Consider a dielectric sphere placed in a uniform electric field 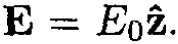 Since the field at infinity is
Since the field at infinity is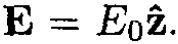 and the field produced by the sphere must be a dipole field, try a solution outside the sphere:
and the field produced by the sphere must be a dipole field, try a solution outside the sphere:
 (1)
(1)
Inside the sphere, try a field oriented in the direction of the original field E0:
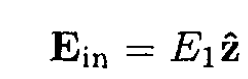 (2)
(2)
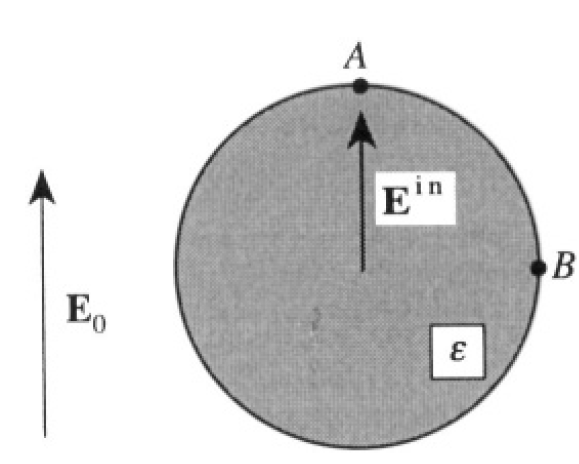
Figure 1.1
The usual boundary conditions apply:
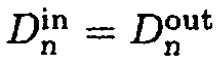 (3)
(3)
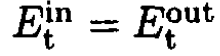 (4)
(4)
Taking (3) and (4) at points A and B, respectively (see Figure 1.1),
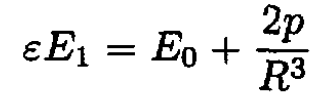 (5)
(5)
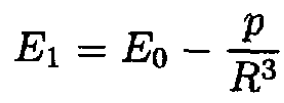 (6)
(6)
Solving (5) and (6) for yields
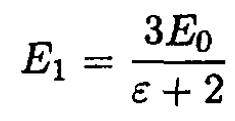 (7)
(7)
so
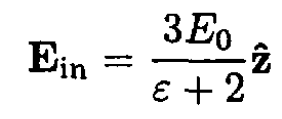
The dipole moment p is found by substituting (7) back into (6):
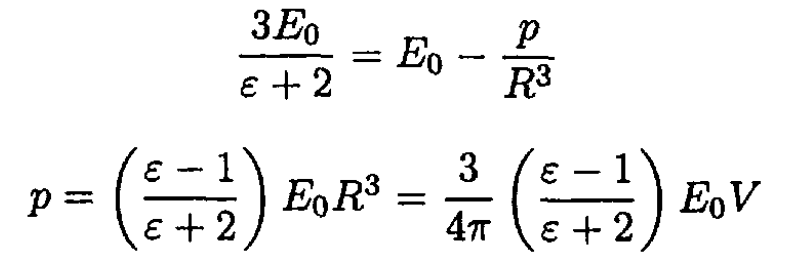
Using the condition nR2 << 1 (low concentration of particles), we can disregard the interaction between them. The polarization of the medium then is given by the dipole moment per unit volume. Here, we have n dipoles per unit volume, so
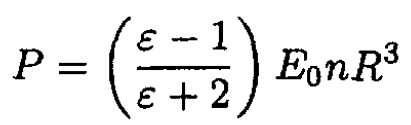 (8)
(8)
Now, D = ε' E0 = E0 +4πP, so
 (9)
(9)
The apparent but wrong answer ε' = 1 + (ε – 1)nV comes about by neglecting the shape of the particles and considering ε' as the average of the dielectric constant of free space, 1, and the dielectric constant of the spheres, ε.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ندوات وأنشطة قرآنية مختلفة يقيمها المجمَع العلمي في محافظتي النجف وكربلاء
|
|
|