

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Self-Ionization of Water and the pH Scale
المؤلف:
ADAM RENSLO
المصدر:
the organic chemistry of medicinal agent
الجزء والصفحة:
p241
23-6-2016
2668
Self-Ionization of Water and the pH Scale
The observation that pure water has low levels of H+ and OH− is easily understood by the Brønsted–Lowry theory. In this self-ionization behavior, one molecule of water acts as the proton donor (acid) and a second molecule acts as the proton acceptor (base) to generate hydroxide and a hydronium ion (H3O+).
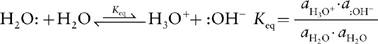
As noted in the equation above, thermodynamic equilibrium constants (Keq) are formally defined by the activities (ai) of each species. However, for dilute solutions where the solvent is in vast excess, the activity of the solvent (water in this case) is unity (aH2O = 1) and the activities for the dilute ions are essentially equal to their molar concentrations (aH3O+ ~ [H3O+], aOH− ~ [:OH−]). As a result, the equilibrium dissociation constant for the self-ionization reaction of water (its acid dissociation constant) is simplified to
Kw = [H3O+][: OH−]
At 25°C, Kw = 10−14 M2, and since the self-ionization reaction yields equal amounts of H3O+ and OH−, both are present at 10−7 M in pure water. As other acids or bases are dissolved in and react with water, the concentrations of H3O+ and OH− re-equilibrate such that their product always equals 10−14. Thus when [H3O+] = 1 M, [OH−] = 10−14 M and vice versa. To simplify discussions of the relative acidity of aqueous solutions, we use the pH scale, where
pH = – log10[H3O+]
For pure water with [H3O+] = 10−7 M, the pH = 7, which is also referred to as neutral pH because the concentrations of H3O+ and OH− ions are equal. Acidic solutions have higher concentrations of H3O+ ([H3O+] > [OH−]) and pH values < 7, whereas basic solutions have lower concentrations of H3O+ ([H3O+] < [OH−]) and pH values > 7.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















