


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 23-1-2018
Date: 26-12-2018
Date: 6-11-2018
|
Dipole moments
Polar diatomic molecules The symmetrical electron distribution in the bond of a homonuclear diatomic renders the bond non-polar. In a heteronuclear diatomic, the electron withdrawing powers of the two atoms may be different, and the bonding electrons are drawn closer towards the more electronegative atom. The bond is polar and possesses an electric dipole moment (µ). Be careful to distinguish between electric and magnetic dipole moments.
The dipole moment of a diatomic XY is given by equation 1.1 where d is the distance between the point electronic charges (i.e. the internuclear separation), e is the charge on the electron (1.602 × 10-19 C) and q is point charge. The SI unit of µ is the coulomb metre (C m) but for convenience, tends to be given in units of debyes (D) where 1D = 3.336 × 10 -30Cm.
µ = q × e × d (1.1)
Worked example: Dipole moments
The dipole moment of a gas phase HBr molecule is 0.827 D. Determine the charge distribution in this diatomic if the bond distance is 141.5 pm. (1D = 3.336 × 10-30Cm) To find the charge distribution we need to find q using the expression:
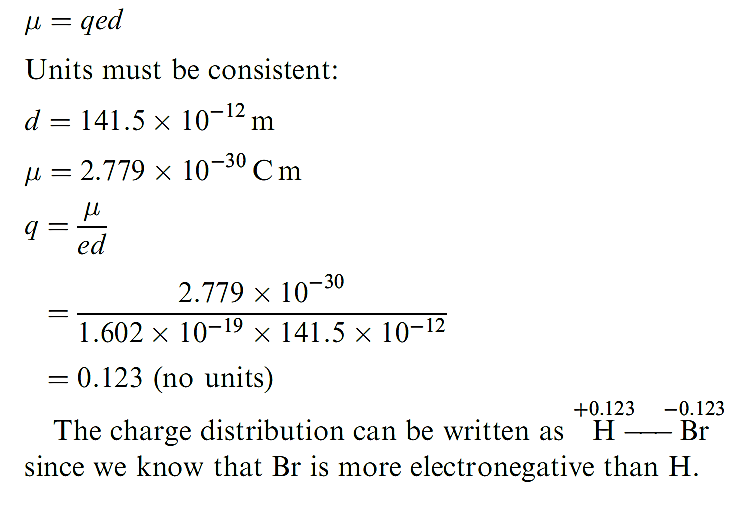
In worked example above the result indicates that the electron distribution in HBr is such that effectively 0.123 electrons have been transferred from H to Br. The partial charge separation in a polar diatomic molecule can be represented by use of the symbols δ+ and δ- assigned to the appropriate nuclear centres, and an arrow represents the direction in which the dipole moment acts. By SI convention, the arrow points from the δ- end of the bond to the end, which is contrary to long-established chemical practice. This is shown for HF in structure 1.14. Keep in mind that a dipole moment is a vector quantity.


A word of caution: attempts to calculate the degree of ionic character of the bonds in heteronuclear diatomics from their observed dipole moments and the moments calculated on the basis of charge separation neglect the effects of any lone pairs of electrons and are therefore of doubtful validity. The significant effects of lone pairs are illustrated below in Example 3. Polarity is a molecular property. For polyatomic species, the net molecular dipole moment depends upon the magnitudes and relative directions of all the bond dipole moments in the molecule. In addition, lone pairs of electrons may contribute significantly to the overall value of µ. We consider three examples below, using the Pauling electronegativity values of the atoms involved to give an indication of individual bond polarities. This practice is useful but must be treated with caution as it can lead to spurious results, e.g. when the bond multiplicity is not taken into account when assigning a value of χ P. Experimental values of molecular electric dipole moments are determined by microwave spectroscopy or other spectroscopic methods.
Example 1: CF4


The values of χ P(C) and χ P(F) are 2.6 and 4.0, respectively, indicating that each C_F bond is polar in the sense
Cδ+_ Fδ-. The CF4 molecule (1.15) is tetrahedral and the four bond moments (each a vector of equivalent magnitude) oppose and cancel one another. The effects of the F lone pairs also cancel out, and the net result is that CF4 is nonpolar.

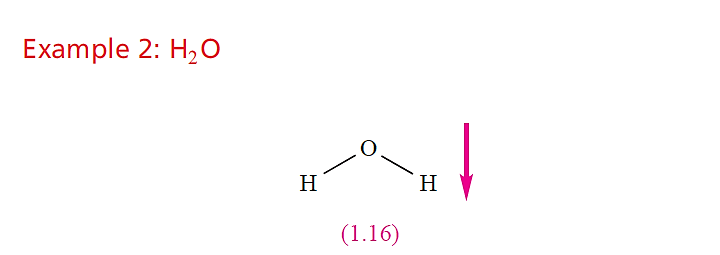
For O and H, χ P = 3.4 and 2.2, respectively, showing that each O–H bond is polar in the sense Oδ-__ H δ+. Since theH2O molecule is non-linear, resolution of the two bond vectors gives a resultant dipole moment which acts in the direction shown in structure 1.16. In addition, the O atom has two lone pairs of electrons which will reinforce the overall moment. The experimental value of µ for H2O in the gas phase is 1.85 D.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|