
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
QUANTUM NATURE OF LIGHT
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
الجزء والصفحة:
p9
8-3-2016
3021
QUANTUM NATURE OF LIGHT
One of the earliest views of what light is was provided by Isaac Newton early in the eighteenth century. Based on the behavior of light in exhibiting reflection and refraction, he postulated that light was a stream of particles. Although this explanation works well for basic optical phenomena, it fails to explain interference. Later experiments, such as Young’s dual-slit experiment, showed that light did indeed have a wavelength and that such behavior could only be explained by using wave mechanics, a concept Newton had argued against a century earlier. By the end of the nineteenth century, wave theory was well accepted but a few glitches remained: namely, the blackbody spectrum of light emitted from heated objects and issues such as the UV catastrophe, upon which classical physics failed. To explain this, Max Planck (the “father” of quantum mechanics) used particle theory once again. He postulated that the atoms in a blackbody acted as tiny harmonic oscillators, each of which had a fundamental quantized energy that obeyed the relationship
E = hv (1.1)
where h is Planck’s constant and v is the frequency of the radiation emitted. This important equation may also be expressed in terms of wavelength as
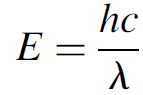 (1.2)
(1.2)
where λ is the wavelength in meters. The ramifications of quantization the fact that the energy of each atom was in integral multiples of this quantity has far reaching ramifications for the entire field of physics (and chemistry), and as we shall see in subsequent chapters, affects our entire view of the atom! Einstein also endorsed this concept of quantization and used it to explain the photoelectric effect, which definitely showed light to exhibit particle properties. These particles of light came to be known as photons, and according to the relationship above, were shown to have a discrete value of energy and frequency (and hence, wavelength). Light can be thought of as a wave that has particle like qualities (or, if you prefer, a particle with wavelike qualities). It was evident from numerous experiments that both wave and particle properties are required to fully explain the behavior of light.
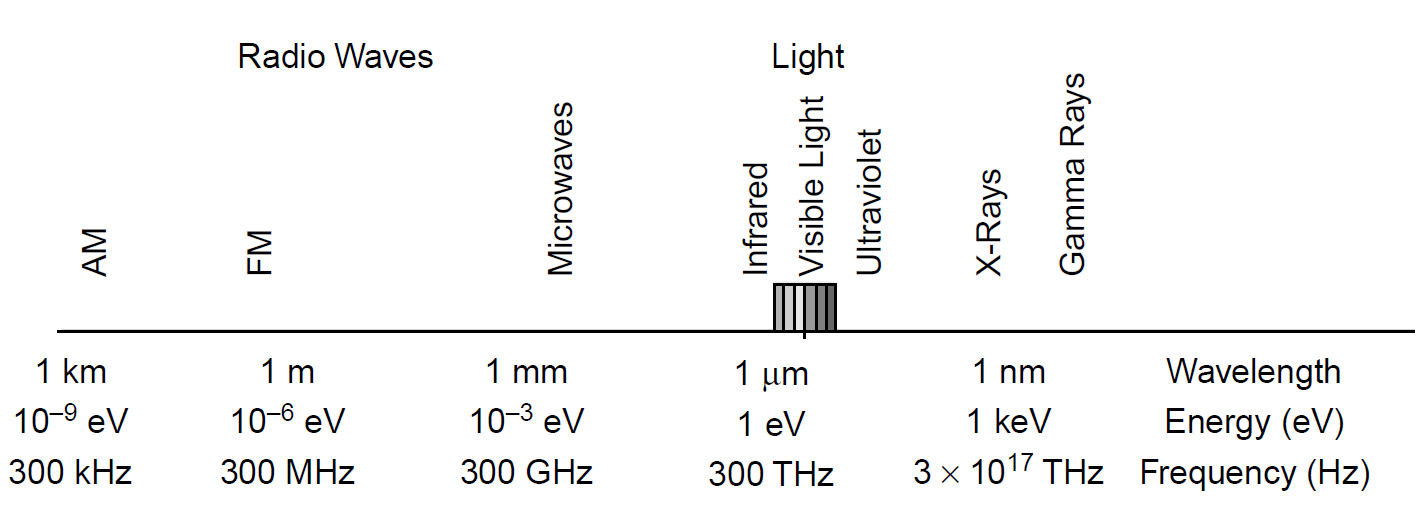

Figure 1.1. Electromagnetic spectrum with energies.
 الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















