
Synchrotron Radiation
 المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
 المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
p26
الجزء والصفحة:
p26
 25-2-2016
25-2-2016
 2407
2407
Synchrotron Radiation
Notwithstanding the vast number of sources of thermal emissions, much of the radiation from our own galaxy, particularly the background radiation first discovered by Jansky, and most of that from other galaxies is of non-thermal origin. The major mechanism behind this type of radiation has nothing to do with temperature, but rather with the effect of charged particles interacting with magnetic fields. When a charged particle enters a magnetic field, the field compels it to move in a circular or spiral path around the magnetic lines of force. The particle is thus accelerated and radiates energy. Under non-relativistic conditions (that is, when particle velocities are well-below the speed of light), this cyclotron radiation is not strong enough to have much astronomical importance. However, when the speed of the particle reaches nearly the speed of light, it emits a much stronger form of cyclotron radiation called synchrotron radiation.
Emission of Synchrotron Radiation
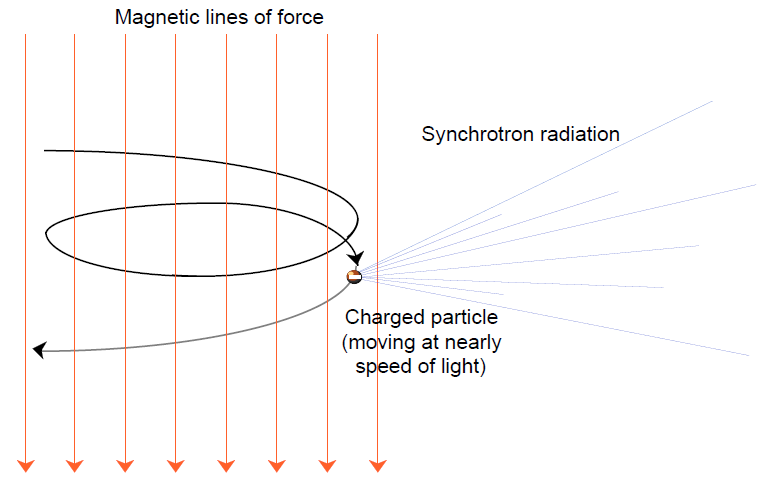
Quasars are one source of synchrotron radiation not only at radio wavelengths, but also at visible and x-ray wavelengths.
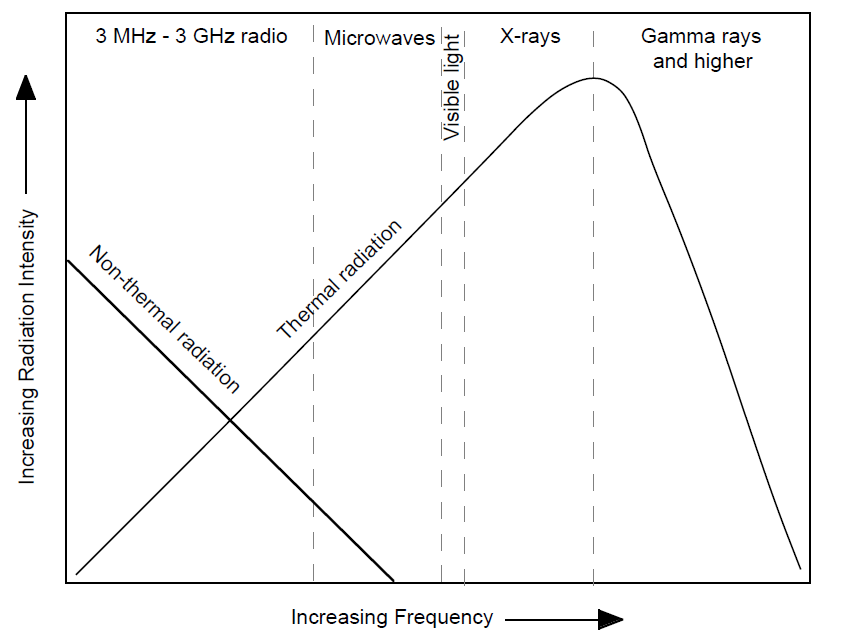
An important difference in radiation from thermal versus non-thermal mechanisms is that while the intensity (energy) of thermal radiation increases with frequency, the intensity of non-thermal radiation usually decreases with frequency.
Relative Variation of Thermal and Non-thermal Radiation Emissions
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


