

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
Two Interesting Examples
المؤلف:
W.D. Wallis
المصدر:
Mathematics in the Real World
الجزء والصفحة:
38-39
14-2-2016
2207
Probabilities can sometimes be surprising. We shall discuss two examples.
Birthday Probabilities
Suppose there are 30 people in a room. What is the probability that two of them share the same birthday (day and month)? (For simplicity, we shall ignore leap years.) Most people would say at first that the probability is small, but this is wrong.
First, list the 30 peoples’ birthdays in the order of their names (alphabetical order). If there is no restriction, each person has 365 possible birthdays. So there are 36530 possibilities.
Suppose no two of them have the same birthday. There are 365 choices for the first person’s birthday, 364 for the second, 363 for the third, and so on. With no repeats the total number of possible lists of birthdays is
365×364×...×336.
Therefore the probability of the event “no two have the same birthday” is
365×364×...×336/36530
which is approximately .294. So the probability of the “birthday coincidence” is about
1−.294 = .706,
or approximately 70%.
The Game Show
Our second example was made popular by columnist Marilyn Vos Savant.
Consider a TV game show: the contestant chooses between three doors marked doors 1, 2, and 3. Behind one door is a new car; behind each other is something almost worthless (a week’s supply of Kleenex tissues; two movie tickets; a pet goat)—call it a booby prize. The contestant chooses a door, and she gets the prize behind it.
But wait! After the choice is announced but before door is opened, the host opens one of the other two doors (not the one the contestant chose). Behind the door we see a goat. The host then asks, “Do you want to stay with your original choice? Or would you rather switch to the third door?”
Well, should the contestant stay or switch? Or doesn’t it matter? Most people would say it doesn’t matter.
To analyze the problem, we need to agree on a few things.
1. On any given night the chance that the car is behind any particular door is one in three.
2. The host always opens a door to show a goat, then offers the switch.
3. If the contestant’s first choice is the door with the car, there is an equal chance that the host will open either of the other two doors. He doesn’t open the lowernumbered one more often, or anything like that.
4. The game is always played the same way (the host never skips the “open another door” part).
For ease of analysis, suppose the doors are numbered 1, 2, and 3. The contestant chooses door 1. We shall write C1 to mean “the car is behind door 1,” C2 for “car behind door 2,” and C3 for “car behind door 3.” Similarly, H2 means “host opens door 2”, and H3 means “host opens door 3”. (He will not ever open door 1.)
Now suppose the game is played 600 times. We expect the car to behind each door in 200 cases. If the car is behind door 1, then we expect the host will open door 2 in 100 cases and open door 3 in 100 cases. In the 200 cases where the car is behind door 2, he always opens door 3; in the 200 cases where the car is behind door 3, he always opens door 2. So we can represent the data by
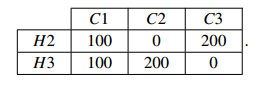
Now suppose the host opens door 2. This tells us that tonight is one of the 300 cases represented in the row H2. Of those 300 cases, the car is behind door 1 in 100 cases and behind door 3 in 200 cases. So the odds in favor of switching are 2 to 1.
The same reasoning applies when he opens door 3. So it is always best to switch.
This problem is based on the game “Let’s Make A = a Deal,” with host Monty Hall, so it is often called the Monty Hall problem. Mr Hall has pointed out that in the real world, the conditions 1–4 do not always apply.
 الاكثر قراءة في الاحتمالات و الاحصاء
الاكثر قراءة في الاحتمالات و الاحصاء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















