


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-03-22
Date: 2024-05-08
Date: 2024-06-11
|
The STRUT vowel may be pronounced as 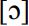 in Channel Island English. Words such as sun or duck are locally realized as
in Channel Island English. Words such as sun or duck are locally realized as 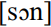 and
and 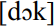 . In comparison to the RP vowel
. In comparison to the RP vowel 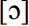 is further back and above all, the vowel is rounded. Parallels to this feature in other varieties are rather difficult to find. In the data of the Survey of English Dialects (SED; Orton 1962–1971),
is further back and above all, the vowel is rounded. Parallels to this feature in other varieties are rather difficult to find. In the data of the Survey of English Dialects (SED; Orton 1962–1971), 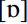 is very occasionally used for the STRUT vowel. In the responses to question IV.6.14 (‘ducks’),
is very occasionally used for the STRUT vowel. In the responses to question IV.6.14 (‘ducks’), 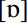 occurs three times in Kent, once in Essex and once in Hampshire. In question IX.2.3 (‘sun’),
occurs three times in Kent, once in Essex and once in Hampshire. In question IX.2.3 (‘sun’), 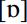 was recorded twice in Kent, once in Wiltshire and once in the Isle of Man. An influence from Norman French seems more likely in this case. Channel Island French does not have a vowel sound comparable to English /Λ/. One can therefore assume that a phone substitution takes place in English, replacing /Λ/ by
was recorded twice in Kent, once in Wiltshire and once in the Isle of Man. An influence from Norman French seems more likely in this case. Channel Island French does not have a vowel sound comparable to English /Λ/. One can therefore assume that a phone substitution takes place in English, replacing /Λ/ by 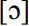 . This hypothesis is confirmed by the fact that the same phone substitution occurs in English loanwords in Channel Island French. Thus, the word bus is pronounced
. This hypothesis is confirmed by the fact that the same phone substitution occurs in English loanwords in Channel Island French. Thus, the word bus is pronounced 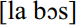 in the local French dialects.
in the local French dialects.
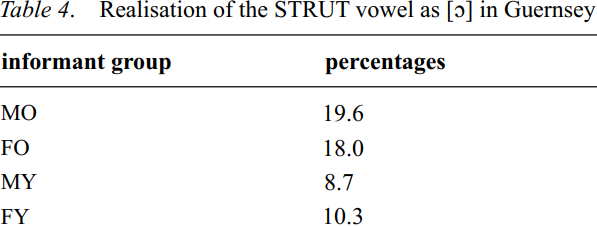
The results for the STRUT vowel among the same 40 informants in Guernsey equally lend support to the hypothesis. The quantitative analysis of the variable shows a generational difference. The older informants (and speakers of Guernsey French) scored about 10% higher than the younger informants (monolingual speakers of English).
|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي يعلن إطلاق المسابقة الجامعية الوطنية لأفضل بحث تخرّج حول القرآن الكريم
|
|
|