

 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 23-10-2015
Date: 16-10-2015
Date: 26-10-2015
|
Plankton
Plankton is small aquatic organisms that live in both freshwater and marine environments. The word “plankton” is derived from the Greek word planktos, which means “drifting.” In general, plankton has little or no means of locomotion and their distribution is determined largely by water currents and mixing. However, some plankton can swim through less turbulent waters using flagella and other appendages.
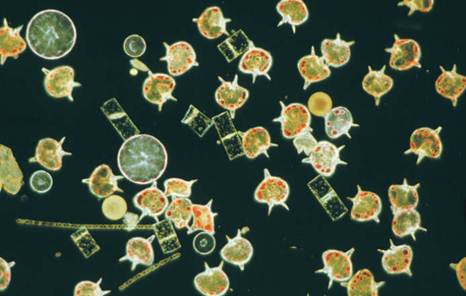
Marine plankton. Plankton are a critical food resource for other aquatic organisms that live in freshwater and marine environments.
There are several broad categories of plankton. Phytoplanktons are small plantlike plankton and are commonly referred to as algae. Phytoplankton is primary producers (they use energy from the sun to make organic food molecules). Bacterioplankton are very small (only seen through a microscope) and include bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Some bacterioplankton play important roles as primary producers and others as decomposers. Zooplankton are planktonic invertebrate animals (for example, the water- flea Daphnia). Some zooplanktons consume phytoplankton, whereas others are predatory and consume smaller zooplankton. Ichthyoplankton are plank- tonic fish eggs and larvae. The ichthyoplankton are highly vulnerable to predation by invertebrate and vertebrate predators.
Plankton is important because they form the base of aquatic food webs. That is, plankton is a critical food resource for other aquatic organisms (such as fish) that live in freshwater and marine environments. Plankton is important to humans because they support recreational and commercial fisheries. Some humans consume plankton directly in the form of dietary supplements. For example, the phytoplankton species Spirulina has been marketed as a source of vitamins and protein.
Plankton is also important in processes that control the distribution and movement of energy and essential nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. A significant amount of the total global carbon is stored in the ocean. Some researchers have proposed that it is possible to increase the uptake of carbon dioxide generated by human combustion of fossil fuels by increasing production of ocean plankton through fertilization. Researchers debate whether this proposal is practical at a large scale.
References
Hutchinson, G. Evelyn. A Treatise on Limnology, vol. 2. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1967.
Smith, DeBoyd L. A Guide to Marine Coastal Plankton and Marine Invertebrate Larvae. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company, 1996.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|