
head (n.)
 المؤلف:
David Crystal
المؤلف:
David Crystal
 المصدر:
A dictionary of linguistics and phonetics
المصدر:
A dictionary of linguistics and phonetics
 الجزء والصفحة:
225-8
الجزء والصفحة:
225-8
 2023-09-16
2023-09-16
 1386
1386
head (n.)
A term used in the GRAMMATICAL description of some types of PHRASE (ENDOCENTRIC phrases) to refer to the central element which is DISTRIBUTIONALLY equivalent to the phrase as a whole; sometimes abbreviated as H. Such constructions are sometimes referred to as headed (as opposed to non-headed) or as head phrases (HP). Headedness also determines any relationships of CONCORD or GOVERNMENT in other parts of the phrase or SENTENCE. For example, the head of the NOUN phrase a big man is man, and it is the singular form of this ITEM which relates to the co-occurrence of singular verb forms, such as is, walks, etc.; the head of the VERB phrase has put is put, and it is this verb which accounts for the use of OBJECT and ADVERBIAL later in the sentence (e.g. put it there). In phrases such as men and women, either item could be the head. Since the early 1980s, the term has also been extended to the analysis of WORD-FORMATION, such as in COMPOUNDS: the head of a word is the element which determines the grammatical properties of the whole word. In GENERALIZED PHRASE-STRUCTURE GRAMMAR, the term is used in a more abstract way, as a device which enables one to identify a cluster of related FEATURE specifications which need to be referred to for a particular purpose (such as N, V, AUX, PER (= person) and SLASH).
The head-feature convention, in this context, refers to a principle which determines the feature specifications of the subconstituents of a phrase: it states that the head features on a mother category are the same as the head features on any daughter which is a head. The head parameter is a principle used in GENERATIVE SYNTAX, especially in relation to UNIVERSAL grammar, which concerns the position of heads with respect to their COMPLEMENTS within phrases. It asserts that a language has the heads on the same side in all phrases: head-first languages are represented by English, e.g. kick the ball (the verb in the verb phrase is to the left of the noun phrase) and in the box (the PREPOSITION in the prepositional phrase is to the left of the noun phrase); head-last languages are represented by Japanese or Korean, where the heads appear on the right (e.g. Korean Seoul-eseo ‘in Seoul’). In METRICAL PHONOLOGY, left-headed feet are those where the leftmost RHYME of the FOOT is STRESSED; right-headed feet are those where the rightmost rhyme is stressed. In head-marked metrical NOTATION, these cases are distinguished by placing the NODE representing the foot CONSTITUENT geometrically above the head (i.e. on the rhyme that is stressed), as follows:
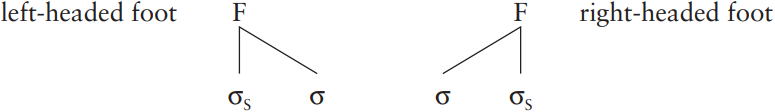
Head is used in some analyses of TONE GROUP structure, referring to the sequence of syllables between the first STRESSED syllable and the NUCLEAR tone; for example, in the tone group there’s a com cpletely cnew arràngement/ the head is -pletely new a-.
 الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


