

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Agreement, case and movement Summary
المؤلف:
Andrew Radford
المصدر:
Minimalist Syntax
الجزء والصفحة:
322-8
31-1-2023
1593
Agreement, case and movement Summary
We have taken a look at Chomsky’s recent work on case, agreement and A-movement. We saw that agreement plays an integral role in nominative case assignment, in that nominative case is assigned to a nominal which agrees in person and number with a finite T. We argued that some features enter the derivation already valued (e.g. the tense feature of T and the person/number 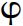 -features of nominals), whereas others (e.g. the
-features of nominals), whereas others (e.g. the  -features of T and the case feature of nominals) are initially unvalued and are assigned values in the course of the derivation by operations like Feature-Copying (7) and Nominative Case Assignment (9). We claimed that interpretable features enter the derivation already valued, whereas those features which are initially unvalued are uninterpretable. We saw that agreement and case-marking involve a relation between an active probe and an active goal, and that probe and goal are only active if they carry one or more uninterpretable features (e.g. uninterpretable
-features of T and the case feature of nominals) are initially unvalued and are assigned values in the course of the derivation by operations like Feature-Copying (7) and Nominative Case Assignment (9). We claimed that interpretable features enter the derivation already valued, whereas those features which are initially unvalued are uninterpretable. We saw that agreement and case-marking involve a relation between an active probe and an active goal, and that probe and goal are only active if they carry one or more uninterpretable features (e.g. uninterpretable  -features or case features). We also saw that uninterpretable features have to be deleted in the course of the derivation by a Feature-Deletion operation (14), in order to ensure that they do not feed into the semantic component and thereby cause the derivation to crash (because they are illegible in the semantic component), and that only a
-features or case features). We also saw that uninterpretable features have to be deleted in the course of the derivation by a Feature-Deletion operation (14), in order to ensure that they do not feed into the semantic component and thereby cause the derivation to crash (because they are illegible in the semantic component), and that only a  -complete
-complete 
 can delete an uninterpretable feature of ß. We suggested that expletive it enters the derivation with uninterpretable third-person and singular-number features, and that these value, delete and in turn are deleted by those of the auxiliary in sentences such as It is said that he has taken bribes. However, we noted that weather it is quasi-referential, and may originate as an argument internally within VP. We looked at Chomsky’s claim that there is merged directly in spec-TP, and serves as a probe whose uninterpretable third-person feature is deleted via agreement with a
can delete an uninterpretable feature of ß. We suggested that expletive it enters the derivation with uninterpretable third-person and singular-number features, and that these value, delete and in turn are deleted by those of the auxiliary in sentences such as It is said that he has taken bribes. However, we noted that weather it is quasi-referential, and may originate as an argument internally within VP. We looked at Chomsky’s claim that there is merged directly in spec-TP, and serves as a probe whose uninterpretable third-person feature is deleted via agreement with a  -complete T. We noted that such an analysis has consequences (for the nature of probes and the inactivation of features) which may not seem desirable, and outlined an alternative analysis of expletives as originating within VP. We outlined Chomsky’s agreement-based theory of movement under which movement involves an agreement relation between an active probe with an [EPP] feature and an active goal, and we suggested in (45) that the [EPP] feature of T can be satisfied either by merger of an expletive in spec-TP, or by movement of the closest active matching goal to spec-TP, with merger/movement of the relevant constituent in spec-TP deleting the [EPP] feature of T. We looked at the syntax of control infinitives, claiming that their PRO subject is assigned null case via agreement with a
-complete T. We noted that such an analysis has consequences (for the nature of probes and the inactivation of features) which may not seem desirable, and outlined an alternative analysis of expletives as originating within VP. We outlined Chomsky’s agreement-based theory of movement under which movement involves an agreement relation between an active probe with an [EPP] feature and an active goal, and we suggested in (45) that the [EPP] feature of T can be satisfied either by merger of an expletive in spec-TP, or by movement of the closest active matching goal to spec-TP, with merger/movement of the relevant constituent in spec-TP deleting the [EPP] feature of T. We looked at the syntax of control infinitives, claiming that their PRO subject is assigned null case via agreement with a  -complete T carrying null (non-finite) tense. We went on to argue that data relating to the distribution of floating modifiers suggest that T in control clauses has an [EPP] feature which triggers movement of PRO to spec-TP. We argued that T in other kinds of infinitive clause (e.g. the infinitival complements of raising, passive and ECM predicates) is defective in that although it carries uninterpretable [EPP] and person features (the latter serving to make T active), it lacks the number feature carried by a
-complete T carrying null (non-finite) tense. We went on to argue that data relating to the distribution of floating modifiers suggest that T in control clauses has an [EPP] feature which triggers movement of PRO to spec-TP. We argued that T in other kinds of infinitive clause (e.g. the infinitival complements of raising, passive and ECM predicates) is defective in that although it carries uninterpretable [EPP] and person features (the latter serving to make T active), it lacks the number feature carried by a  -complete T in finite and control clauses. We saw that such an analysis entails that A-movement takes place in a successive-cyclic fashion, with the moved argument being raised to become the subject of a lower TP before raising to become the subject of a higher TP. We went on to consider the possibility that all movement operations are local (and hence apply in a successive-cyclic fashion in complex structures) and noted that this implies that A-bar movement operations like wh-movement are also successive-cyclic in complex sentences (but said we would postpone detailed discussion of this).
-complete T in finite and control clauses. We saw that such an analysis entails that A-movement takes place in a successive-cyclic fashion, with the moved argument being raised to become the subject of a lower TP before raising to become the subject of a higher TP. We went on to consider the possibility that all movement operations are local (and hence apply in a successive-cyclic fashion in complex structures) and noted that this implies that A-bar movement operations like wh-movement are also successive-cyclic in complex sentences (but said we would postpone detailed discussion of this).
 الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















