

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Addition of Other Reagents to Unsymmetrical Alkenes. The Electronegativity Chart
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
18-1-2022
3062
Addition of Other Reagents to Unsymmetrical Alkenes. The Electronegativity Chart
We can extend Markownikoff's rule to cover additions of substances of the general type X−Y to unsymmetrically substituted alkenes when a clear-cut decision is possible as to whether X or Y is the more electrophilic atom of X−Y. If the polarization of the X−Y bond is such that X is positive, δ⊕X−Yδ⊖, then XX will be expected to add as X⊕ to the alkene to form the more stable carbocation. This step will determine the direction of addition. For example, if we know that the O−Br bond of HOBr is polarized as HOδ⊖−Brδ⊕, then we can predict that addition of HOBr to 2-methylpropene will give 1-bromo-2-methyl-2-propanol:
Figure 10-11), the elements of each horizontal row in the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing electronegativity from left to right. In a given horizontal row of the periodic table, electronegativity increases with increasing atomic number. However, electronegativity decreases with increasing atomic number in a given vertical column of the periodic table.
Figure 10-11: Pauling electronegativities of elements. The dashed lines connect elements in particular vertical columns of the periodic table.
Pauling's value for the electronegativity of carbon makes it slightly more electron-attracting than hydrogen. However, we expect that the electron-attracting power of a carbon atom (or of other elements) will depend also on the electronegativities of the groups to which it is attached. In fact, many experimental observations indicate that carbon in methyl or other alkyl groups is significantly less electron-attracting than hydrogen. Conversely, the CF3− group is, as expected, far more electron-attracting than hydrogen.
The direction of polarization of bonds between various elements may be predicted from Figure 10-11. For example, an O−Cl bond should be polarized so the oxygen is negative; a C−N bond should be polarized so the nitrogen is negative:
We then can predict that, in the addition of HOCl to an alkene, the chlorine will add preferentially to form the more stable of two possible carbon cations. Generally, this means that chlorine will bond to the carbon carrying the greater number of hydrogens:
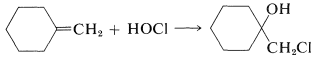
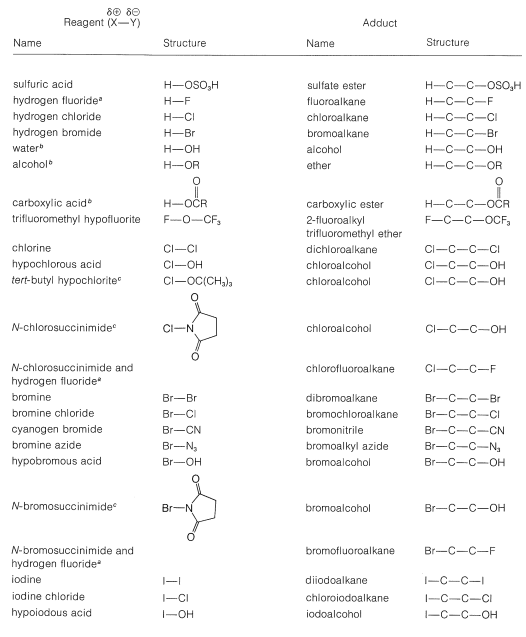
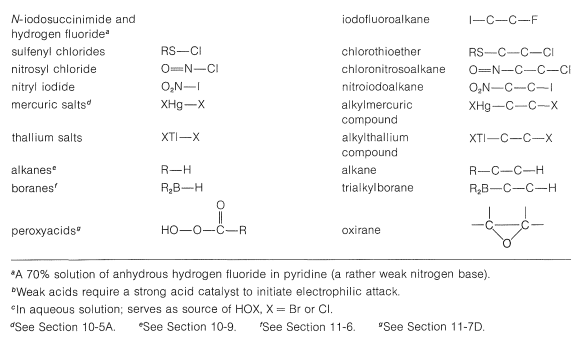
A number of reagents that are useful sources of electrophilic halogen are included in Table 10-2. Some of these reagents, notably those with O−halogen or N−halogen bonds, actually are sources of hypohalous acids, HOX, and function to introduce halogen and hydroxyl groups at carbon. There are very few good fluorinating agents whereby the fluorine is added as F⊕.
Table 10-2: Reagents that add to Alkenes by Electrophilic Attack:
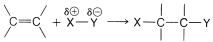
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















