


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 22-2-2020
Date: 14-8-2019
Date: 22-2-2020
|
You may have wondered why the hydroxyl proton of ethanol produces a single resonance in the spectrum of Figure 9-23. It is quite reasonable to expect that the hydroxyl proton would be split by the neighboring methylene protons because they are only three bonds apart, 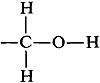 however, this coupling will not be observed if the hydroxyl protons are exchanging rapidly between the ethanol molecules. When proton exchange is rapid, the spin interactions between the −CH2− and −OH protons average to zero. At intermediate exchange rates, the coupling manifests itself through line broadening or by actually giving multiple lines. If you look at the several spectra of ethanol in Figure 9-29, you will notice how the shape of the OH resonance varies from a broad singlet to a distinct triplet.
however, this coupling will not be observed if the hydroxyl protons are exchanging rapidly between the ethanol molecules. When proton exchange is rapid, the spin interactions between the −CH2− and −OH protons average to zero. At intermediate exchange rates, the coupling manifests itself through line broadening or by actually giving multiple lines. If you look at the several spectra of ethanol in Figure 9-29, you will notice how the shape of the OH resonance varies from a broad singlet to a distinct triplet.
Rapid chemical exchange of magnetic nuclei is not the only way that spin-coupling interactions can be averaged to zero. The same effect can be achieved by a technique known as double resonance. To understand how this is done, consider two coupled protons HA and HB having different chemical shifts. Suppose that HA is selectively irradiated at its resonance frequency νA while at the same time we observe the resonance signal of HB. The coupling between HA and HB disappears, and HB shows a single resonance. Why is this so? By irradiation of HA, the HA nuclei are changed from the +1/2 state to -1/2 and back again sufficiently rapidly that the neighboring nucleus HB effectively “sees” neither one state nor the other. The magnetic interaction between the states therefore averages to zero. This decoupling of magnetic nuclei by double resonance techniques is especially important in C13 NMR spectroscopy but also is used to simplify proton spectra by selectively removing particular couplings.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|