

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Stereochemistry of SN1 Reactions
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
5-1-2022
2399
Stereochemistry of SN1 Reactions
When an SN1 reaction is carried out starting with a single pure enantiomer, such as D-2-chlorobutane, the product usually is a mixture of the enantiomeric substitution products with a slight predominance of that isomer which corresponds to inversion. Theoretically, a carbocation is expected to be most stable in the planar configuration and hence should lead to exactly equal amounts of the two enantiomers, regardless of the chiral configuration of the starting material (Figure 8-3). However, the extent of configuration change that actually results in an SN1 reaction depends upon the degree of "shielding" of the front side of the reacting carbon by the leaving group and its associated solvent molecules. If the leaving group does not get away from the carbocation before the product-determining step takes place, there will be some preference for nucleophilic attack at the back side of the carbon, which results in a predominance of the product of inverted configuration.
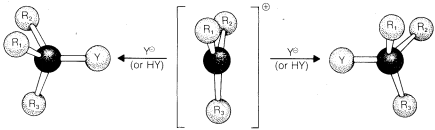
Other things being equal, the amount of inversion decreases as the stability of the carbocation intermediate increases, because the more stable the ion the longer is its lifetime, and the more chance it has of getting away from the leaving anion and becoming a relatively "free" ion. The solvent usually has a large influence on the stereochemical results of SN1 reactions because the stability and lifetime of the carbocations depend upon the nature of the solvent .
An orbital picture of SN1 ionization leading to a racemic product may be drawn as follows:
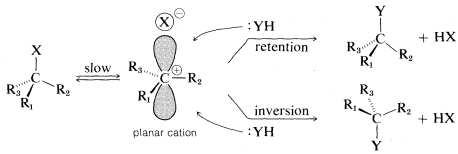
It should be clear that complete racemization is unlikely to be observed if X⊖ stays in close proximity to the side of the positive carbon that it originally departed from. We can say that X⊖ "shields" the front side, thereby favoring a predominance of inversion. If X⊖ gets far away before :YH comes in, then there should be no favoritism for one or the other of the possible substitutions.
If X⊖ and the carbocation, R⊕, stay in close proximity, as is likely to be the case in a solvent that does not promote ionic dissociation, then a more or less "tight" ion pair is formed, R⊕⋅⋅⋅X⊖. Such ion pairs often play an important role in ionic reactions in solvents of low dielectric constant .
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















