


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 2023-07-27
التاريخ: 29-7-2018
التاريخ: 29-5-2017
التاريخ: 29-8-2019
|
The problem of determining whether a particular isomer of C2H4Br2 is

could be solved today in a few minutes by spectroscopic means, as will be explained in Chapter 9. However, at the time structure theory was being developed, the structure had to be deduced on the basis of chemical reactions, which could include either how the compound was formed or what it could be converted to. A virtually unassailable proof of structure, where it is applicable, is to determine how many different substitution products each of a given group of isomers can give. For the C2H4Br2 pair of isomers, substitution of a bromine for a hydrogen will be seen to give only one possibility with one compound and two with the other:
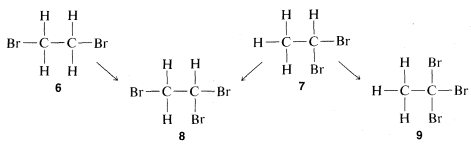
Therefore, if we have two bottles, one containing one C2H4Br2 isomer and one the other and run the substitution test, the compound that gives only one product is 6 and the one that gives a mixture of two products is 7. Further, it will be seen that the test, besides telling which isomer is 6 and which is 7, establishes the structures of the two possible C2H3Br3 isomers, 8 and 9. Thus only 8 can be formed from both of the different C2H4Br2 isomers whereas 9 is formed from only one of them.
There were already many interconversion reactions of organic compounds known at the time that valence theory, structural formulas, and the concept of the tetrahedral carbon came into general use. As a result, it did not take long before much of organic chemistry could be fitted into a concordant whole. One difficult problem was posed by the structures of a group of substitution products of benzene, C6H6, called "aromatic compounds," which for a long time defied explanation. Benzene itself had been prepared first by Michael Faraday, in 1825. An ingenious solution for the benzene structure was provided by A. Kekule, in 1866, wherein he suggested (apparently as the result of a hallucinatory perception) that the six carbons were connected in a hexagonal ring with alternating single and double carbon-to-carbon bonds, and with each carbon connected to a single hydrogen, 1010:
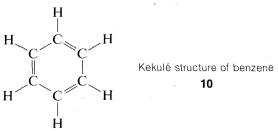
This concept was controversial, to say the least, mainly on two counts. Benzene did not behave as expected, as judged by the behavior of other compounds with carbon-to-carbon double bonds and also because there should be two different dibromo substitution products of benzene with the bromine on adjacent carbons (11 and 12) but only one such compound could be isolated.
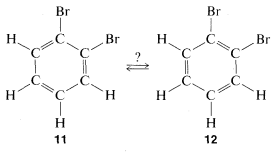
Kekule explained the second objection away by maintaining that 11 and 12 were in rapid equilibrium through concerted bond shifts, in something like the same manner as the free-rotation hypothesis mentioned previously:
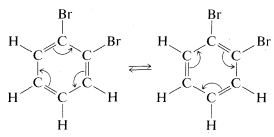
However, the first objection could not be dismissed so easily and quite a number of alternative structures were proposed over the ensuing years. The controversy was not really resolved until it was established that benzene is a regular planar hexagon, which means that all of its C−C bonds have the same length, in best accord with a structure written not with double, not with single, but with 1.5 bonds between the carbons, as in 13:
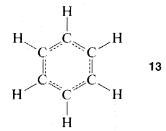
This. in turn, generated a massive further theoretical controversy over just how 13 should be interpreted, which, for a time, even became a part of "Cold-War" politics! We shall examine experimental and theoretical aspects of the benzene structure in some detail later. It is interesting that more than 100 years after Kekule's proposal the final story on the benzene structure is yet to be told.55
The combination of valence theory and the substitution method gives, for many compounds, quite unequivocal proofs of structure. Use of chemical transformations for proofs of structure depends on the applicability of a simple guiding principle, often called the "principle of least structural change." As we shall see later, many exceptions are known and care is required to keep from making serious errors. With this caution, let us see how the principle may be applied. The compound C2H5Br reacts slowly with water to give a product of formula C2H6O. The normal valence of oxygen is two, and we can write two, and only two, different structures, 19 and 20 , for C2H6O:
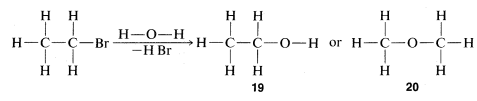
The principle of least structural change favors 19 as the product, because the reaction to form it is a simple replacement of bromine bonded to carbon by −OH, whereas formation of 20 would entail a much more drastic rearrangement of bonds. The argument is really a subtle one, involving an assessment of the reasonableness of various possible reactions. On the whole, however, it works rather well and, in the specific case of the C2H6O isomers, is strongly supported by the fact that treatment of 19 with strong hydrobromic acid (HBr) converts it back to C2H5Br. In contrast, the isomer of structure 20 reacts with HBr to form two molecules of CH3Br:
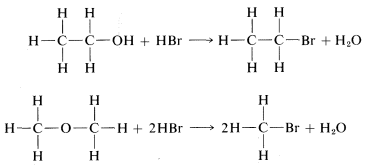
In each case, C−O bonds are broken and C−Br bonds are formed.
We could conceive of many other possible reactions of C2H6O with HBr, for example
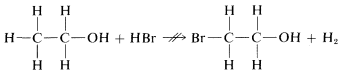
which, as indicated by ↛↛, does not occur, but hardly can be ruled out by the principle of least structural change itself. Showing how the probability of such alternative reactions can be evaluated will be a very large part of our later discussions.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|