

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Structure of Cholesterol
المؤلف:
LibreTexts project
المصدر:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
18-12-2021
2976
Structure of Cholesterol
Although cholesterol was recognized as an individual chemical substance in 1812, all aspects of its structure and stereochemical configuration were not settled until about 1955. The structural problem was a very difficult one, because most of cholesterol is saturated and not easily degraded. Fortunately, cholesterol is readily available, so that it was possible to use rather elaborate degradative sequences, which would have been quite out of the question with some of the rarer natural products.
The first step in the elucidation of the structure of cholesterol was the determination of the molecular formula, first incorrectly as C26H44O in 1859 and then correctly as C27H46O in 1888. The precision required to distinguish between these two formulas is quite high, because C26H44O has 83.80% C and 11.90% H, whereas C27H46O has 83.87% C and 11.99% H. Cholesterol was shown in 1859 to be an alcohol by formation of ester derivatives and in 1868 to possess a double bond by formation of a dibromide. By 1903 the alcohol function was indicated to be secondary by oxidation to a ketone rather than an aldehyde. The presence of the hydroxyl group and double bond when combined with the molecular formula showed the presence of four carbocyclic rings. Further progress was only possible by oxidative degradation.
The structure proof for cholesterol paralleled that for two other important steroids, the so-called bile acids, cholic and desoxycholic acid, which function to help solubilize fats in the intestinal tract. Proof that cholesterol and the bile acids have the same general ring system was achieved by dehydration and reduction of cholesterol to two different hydrocarbons, 5αα-cholestane and 5β-cholestane (coprostane), which differ only in the stereochemistry of the junction between rings A and B:
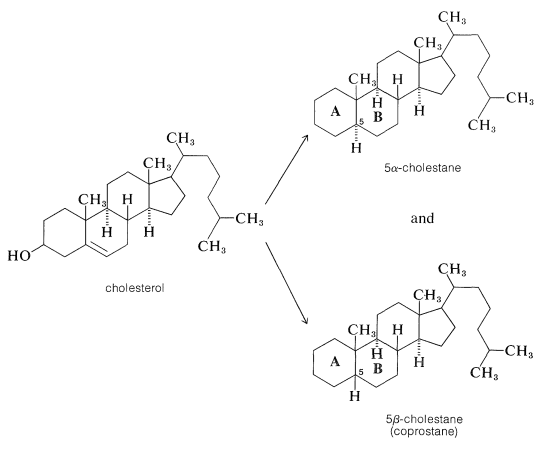
Oxidation of 5β-cholestane, but not 5α-cholestane, gave an acid that turned out to be identical with cholanic acid obtained by dehydration of cholic acid at 300o followed by hydrogenation:
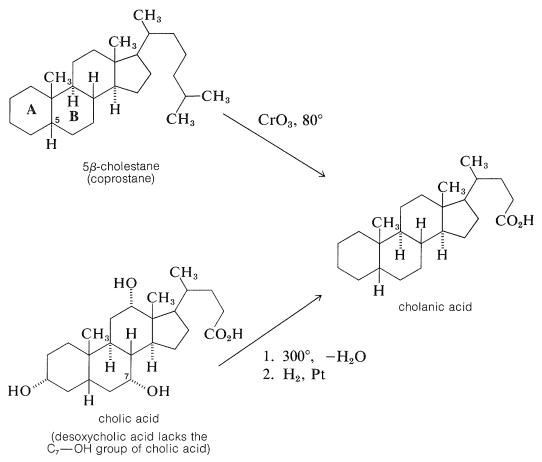
Once the connection between cholesterol and the bile acids was established, further work on the structure proof was directed towards degradation experiments on the bile acids which, with their hydroxyl groups on rings B and C, offered more possible degradation reactions than cholesterol. Outstanding contributions toward the structure proof were made by the German chemists H. Wieland and A. Windaus, both of whom were honored by the award of the Nobel Prize in chemistry. Wieland received the award in 1927 and Windaus in 1928. Despite their many years of effort, the structure proposed by Windaus in 1928 for desoxycholic acid was only tentative and was unspecific as to the location of two carbons.
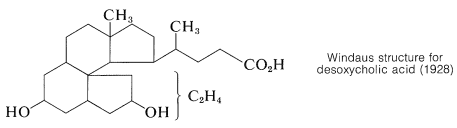
Serious doubt as to the correctness of the Windaus structure came as a result of an x-ray study of ergosterol by J. D. Bernal in 1932. He pointed out that the x-ray evidence indicated ergosterol to be a long, rather flat molecule. Steroids with the ring system corresponding to the Windaus structure would have a globular shape. This observation stimulated further work and a re-examination of the evidence that eventually led to the correct structure. The details of this research may be found elsewhere.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















