
Maple syrup urine disease
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 10-11-2021
10-11-2021
 1957
1957
Maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare (1:185,000), autosomalrecessive disorder in which there is a partial or complete deficiency in BCKD, the mitochondrial enzyme complex that oxidatively decarboxylates leucine, isoleucine, and valine ( Fig. 1). These BCAA and their corresponding α-keto acids accumulate in the blood, causing a toxic effect that interferes with brain functions. The disease is characterized by feeding problems, vomiting, ketoacidosis, changes in muscle tone, neurologic problems that can result in coma (primarily because of the rise in leucine), and a characteristic maple syrup–like odor of the urine because of the rise in isoleucine. If untreated, the disease is fatal. If treatment is delayed, intellectual disability results.
1. Classification: MSUD includes a classic type and several variant forms. The classic, neonatal-onset form is the most common type of MSUD. Leukocytes or cultured skin fibroblasts from these patients show little or no BCKD activity. Infants with classic MSUD show symptoms within the first several days of life. If not diagnosed and treated, classic MSUD is lethal in the first weeks of life. Patients with intermediate forms have a higher level of enzyme activity (up to 30% of normal). The symptoms are milder and show an onset from infancy to adolescence. Patients with the rare thiamine-dependent variant of MSUD respond to large doses of this vitamin.
2. Screening and diagnosis: As with PKU, prenatal diagnosis and newborn screening are available, and most affected individuals are compound heterozygotes.
3. Treatment: MSUD is treated with a synthetic formula that is free of BCAA, supplemented with limited amounts of leucine, isoleucine, and valine to allow for normal growth and development without producing toxic levels. [Note: Elevated leucine is the cause of the neurologic damage in MSUD, and its level is carefully monitored.] Early diagnosis and lifelong dietary treatment are essential if the child with MSUD is to develop normally. [Note: BCAA are an important energy source in times of metabolic need, and individuals with MSUD are at risk of decompensation during periods of increased protein catabolism.]
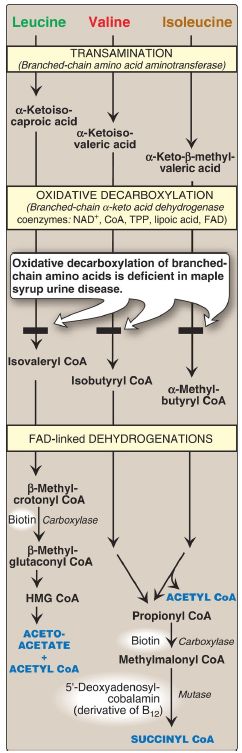
Figure 1: Degradation of leucine, valine, and isoleucine. [Note: β- Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase is one of four biotin-requiring carboxylases . The other three are pyruvate carboxylase, acetyl CoA carboxylase, and propionyl CoA carboxylase.] TPP = thiamine pyrophosphate; FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide; CoA = coenzyme A; NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; HMG = hydroxymethylglutarate.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


