


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 19-11-2021
Date: 3-1-2022
Date: 16-11-2021
|
Branched-chain amino acid degradation
The BCAA isoleucine, leucine, and valine are essential amino acids. In contrast to other amino acids, they are catabolized primarily by the peripheral tissues (particularly muscle), rather than by the liver. Because these three amino acids have a similar route of degradation, it is convenient to describe them as a group (see Fig. 1).
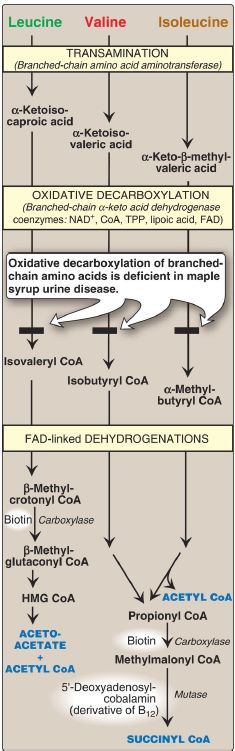
Figure 1: Degradation of leucine, valine, and isoleucine. [Note: β- Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase is one of four biotin-requiring carboxylases discussed in this book. The other three are pyruvate carboxylase, acetyl CoA carboxylase, and propionyl CoA carboxylase.] TPP = thiamine pyrophosphate; FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide; CoA = coenzyme A; NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; HMG = hydroxymethylglutarate.
1. Transamination: Transfer of the amino groups of all three BCAA to α-ketoglutarate is catalyzed by a single, vitamin B6–requiring enzyme, branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase, that is expressed primarily in skeletal muscle.
2. Oxidative decarboxylation: Removal of the carboxyl group of the α-keto acids derived from leucine, valine, and isoleucine is catalyzed by a single multienzyme complex, branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKD) complex. This complex uses thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, oxidized flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), NAD+, and CoA as its coenzymes and produces NADH. [Note: This reaction is similar to the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex and α-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA by the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex . The dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (Enzyme 3, or E3) component is identical in all three complexes.]
3. Dehydrogenations: Oxidation of the products formed in the BCKD reaction produces α-β-unsaturated acyl CoA derivatives and FADH2. These reactions are analogous to the FAD-linked dehydrogenation in the β-oxidation of fatty acids . [Note: Deficiency in the dehydrogenase specific for isovaleryl CoA causes neurologic problems and is associated with a “sweaty feet” odor in body fluids.]
4. End products: The catabolism of isoleucine ultimately yields acetyl Co and succinyl CoA, rendering it both ketogenic and glucogenic. Valine yields succinyl CoA and is glucogenic. Leucine is ketogenic, being metabolized to acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. In addition, NADH and FADH2 are produced in the decarboxylation and dehydrogenation
reactions, respectively. [Note: BCAA catabolism also results in glutamine and alanine being synthesized and sent out into the blood from muscle .]



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|