
Reversible Nonoxidative Reactions
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 27-9-2021
27-9-2021
 1581
1581
Reversible Nonoxidative Reactions
The nonoxidative reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway occur in all cell types synthesizing nucleotides and nucleic acids. These reactions catalyze the interconversion of sugars containing three to seven carbons (see Fig. 1).
These reversible reactions permit ribulose 5-phosphate (produced by the oxidative portion of the pathway) to be converted either to ribose 5-phosphate (needed for nucleotide synthesis) or to intermediates of glycolysis (that is, fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate). For example, many cells that carry out reductive biosynthetic reactions have a greater need for NADPH than for ribose 5-phosphate. In this case, transketolase (which transfers two-carbon units in a thiamine pyrophosphate [TPP]-requiring reaction) and transaldolase (which transfers three-carbon units) convert the ribulose 5-phosphate produced as an end product of the oxidative phase to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate, which are glycolytic intermediates.
In contrast, when the demand for ribose for nucleotides and nucleic acids is greater than the need for NADPH, the nonoxidative reactions can provide the ribose 5- phosphate from glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate in the absence of the oxidative steps (Fig. 2).
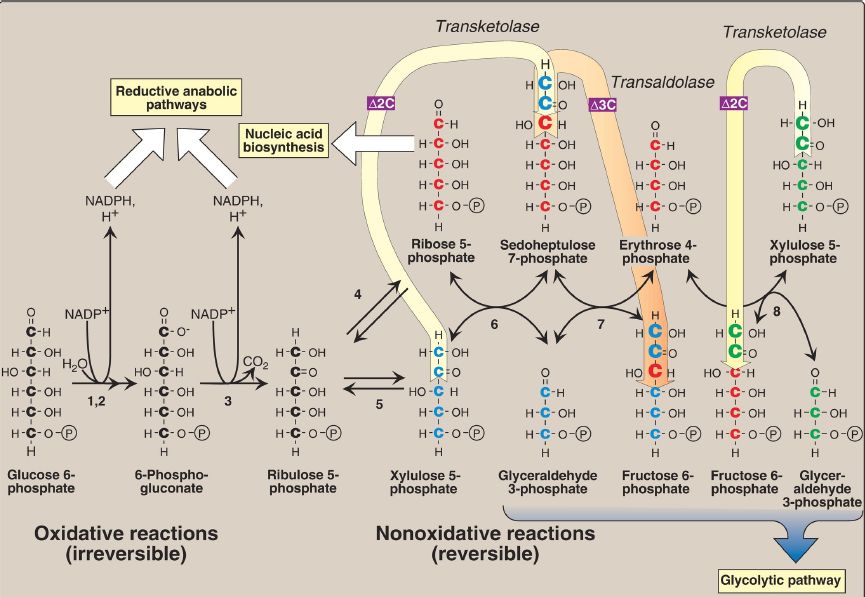
Figure 1: Reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway. Enzymes numbered above are: (1, 2) glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconolactone hydrolase, (3) 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, (4) ribose 5-phosphate isomerase, (5) phosphopentose epimerase, (6, 8) transketolase (coenzyme: thiamine pyrophosphate), and (7) transaldolase. Δ2C = two carbons are transferred from a ketose donor to an aldose acceptor in transketolase reactions; Δ3C = three carbons are transferred in the transaldolase reaction. This can be represented as: 5C sugar + 5C sugar 7C sugar + 3C sugar 4C sugar + 6C sugar. NADP(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; = phosphate; CO2 = carbon dioxide.
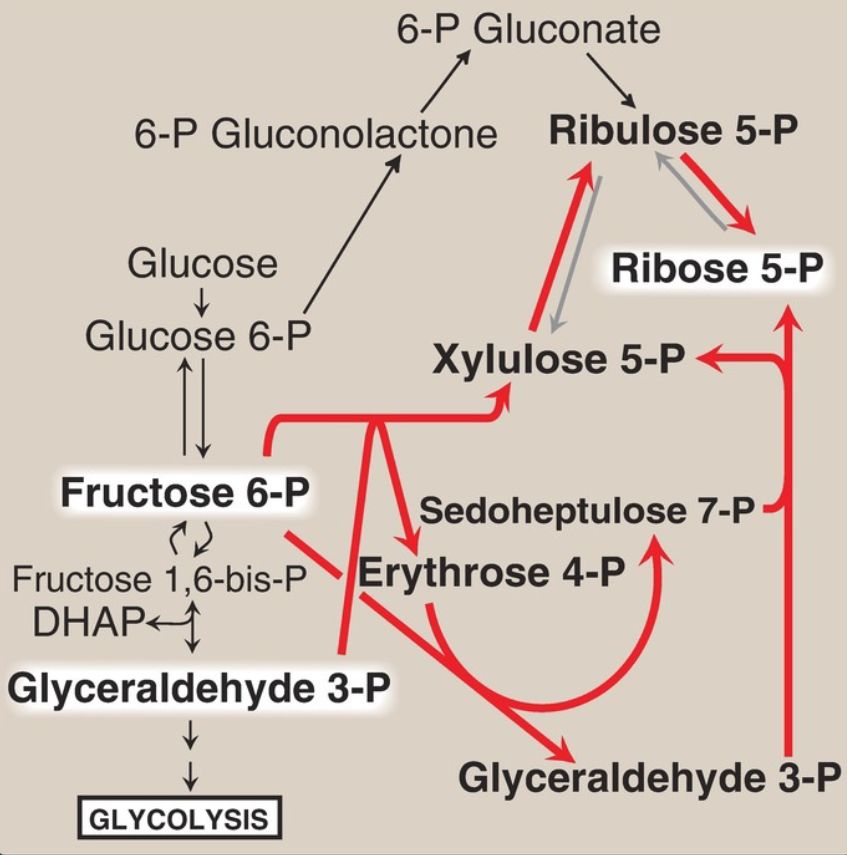
Figure 2: Formation of ribose 5-phosphate from intermediates of glycolysis. P = phosphate; DHAP = dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
In addition to transketolase, TPP is required by the multienzyme complexes pyruvate dehydrogenase (see p. 110), α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase of the tricarboxylic acid cycle , and branchedchain α-keto acid dehydrogenase of branched-chain amino acid catabolism .
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


