
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Vectors in the RC plane
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
الجزء والصفحة:
253
1-5-2021
2232
Vectors in the RC plane
If you work much with engineers, or if you plan to become one, you’ll get familiar with the RC plane, just as you will with the RL plane. Recall from the last chapter that RL impedances can be represented as vectors. The same is true for RC impedances.
There are four different impedance points. Each one is represented by a certain distance to the right of the origin (0,0), and a certain displacement downwards. The first of these is the resistance, R, and the second is the capacitive reactance, Xc. Therefore, the RC impedance is a two-dimensional quantity.
Doesn’t this look like a mirror-image reflection of RL impedances? You could almost imagine that we’re looking at an RL plane reflected in a pool of still water. This is, in fact, an excellent way to envision this situation.
The impedance points in the RC plane can be rendered as vectors, just as this can be done in the RL plane. Then the points become rays, each with a certain length and direction. The magnitude and direction for a vector, and the coordinates for the point, both uniquely define the same impedance value. The length of the vector is the distance of the point from the origin, and the direction is the angle measured clockwise from the resistance (R) line, and specified in negative degrees. The equivalent vectors, are illustrated in Fig. 1.
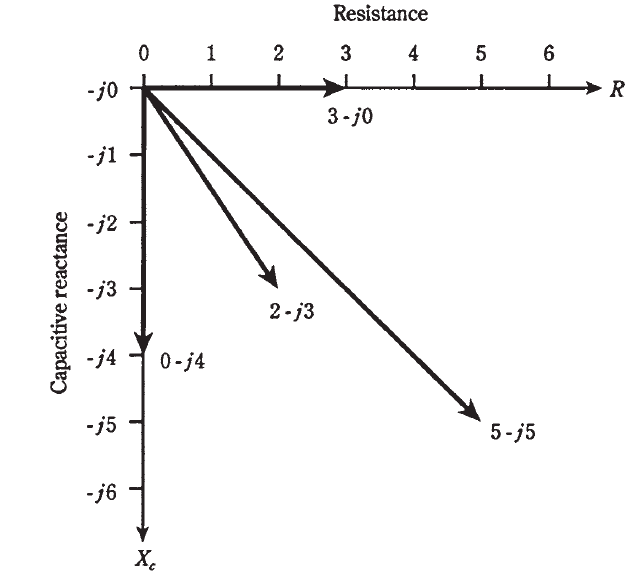
Fig. 1 Four vectors in the RC impedance plane.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















