
The dc motor
 المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
 الجزء والصفحة:
145
الجزء والصفحة:
145
 22-4-2021
22-4-2021
 2605
2605
The dc motor
Magnetic fields can produce considerable mechanical forces. These forces can be harnessed to do work. The device that converts direct-current energy into rotating mechanical energy is a dc motor.
Motors can be microscopic in size, or as big as a house. Some tiny motors are being considered for use in medical devices that can actually circulate in the bloodstream or be installed in body organs. Others can pull a train at freeway speeds.
In a dc motor, the source of electricity is connected to a set of coils, producing magnetic fields. The attraction of opposite poles, and the repulsion of like poles, is switched in such a way that a constant torque, or rotational force, results. The greater the current that flows in the coils, the stronger the torque, and the more electrical energy is needed.
Figure 1 is a simplified, cutaway drawing of a dc motor. One set of coils, called the armature coil, goes around with the motor shaft. The other set of coils, called the field coil, is stationary. The current direction is periodically reversed during each rotation by means of the commutator. This keeps the force going in the same angular direction, so the motor continues to rotate rather than oscillating back and forth. The shaft is carried along by its own inertia, so that it doesn’t come to a stop during those instants when the current is being switched in polarity.
Some dc motors can also be used to generate direct current. These motors contain permanent magnets in place of one of the sets of coils. When the shaft is rotated, a pulsating direct current appears across the coil.
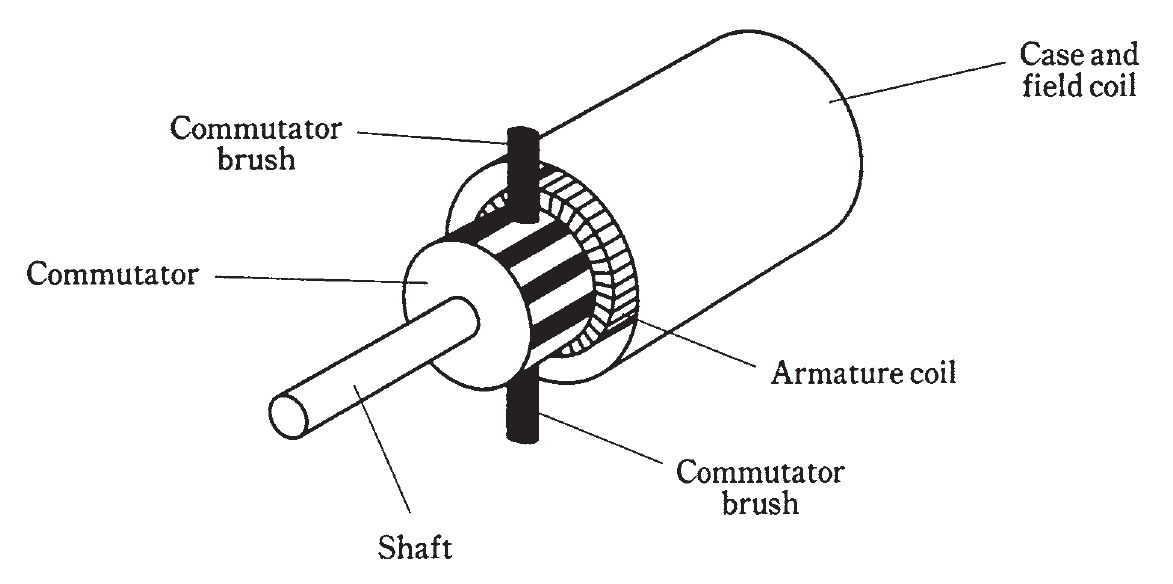
Figure 1: Cutaway view of a dc motor.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


