
How Are Genes and Other Sequences Distributed in the Genome
 المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
 المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 14-3-2021
14-3-2021
 2411
2411
How Are Genes and Other Sequences Distributed in the Genome
KEY CONCEPTS
-Repeated sequences (present in more than one copy) account for more than 50% of the human genome.
-The great bulk of repeated sequences consists of copies of nonfunctional transposons.
-There are many duplications of large chromosome regions.
Are genes uniformly distributed in the genome? Some chromosomes are relatively “gene poor” and have more than 25% of their sequences as “deserts”—regions longer than 500 kb where there are no ORFs. Even the most gene-rich chromosomes have more than 10% of their sequences as deserts. So overall, about 20% of the human genome consists of deserts that have no protein-coding genes.
Repetitive sequences account for approximately 50% of the human genome, as seen in FIGURE 1. The repetitive sequences fall into five classes:
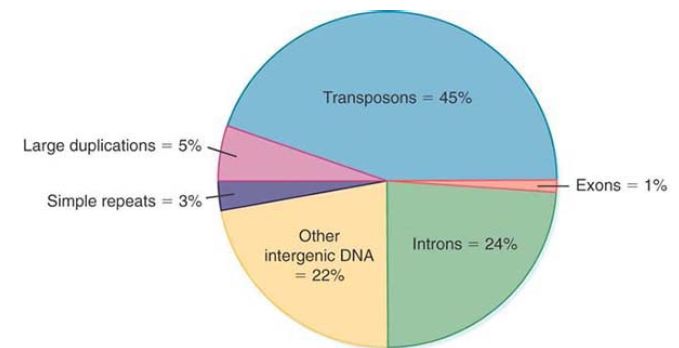
FIGURE 1. The largest component of the human genome consists of transposons. Other repetitive sequences include large duplications and simple repeats.
-Transposons (either active or inactive) account for the majority of repetitive sequences (45% of the genome). All transposons are found in multiple copies.
-Processed pseudogenes, about 3,000 in all, account for about 0.1% of total DNA. (These are sequences that arise by insertion of a reverse transcribed DNA copy of an mRNA sequence into the genome.
- Simple sequence repeats (highly repetitive DNA such as CA repeats) account for about 3% of the genome.
- Segmental duplications (blocks of 10 to 300 kb that have been duplicated into a new region) account for about 5% of the genome. For a small percentage of cases, these duplications are found on the same chromosome; in the other cases, the duplicates are on different chromosomes.
- Tandem repeats form blocks of one type of sequence.
These are especially found at centromeres and telomeres. The sequence of the human genome emphasizes the importance of
transposons. Many transposons have the capacity to replicate themselves and insert into new locations. They can function exclusively as DNA elements or can have an active form that is
RNA (see the chapter titled Transposable Elements and Retroviruses). Most of the transposons in the human genome are nonfunctional; very few are currently active. However, the high proportion of the genome occupied by these elements indicates that they have played an active role in shaping the genome. One interesting feature is that some currently functional genes originated as transposons and evolved into their present condition after losing the ability to transpose. At least 50 genes appear to have originated in this manner.
Segmental duplication at its simplest involves the tandem duplication of some region within a chromosome (typically because of an aberrant recombination event at meiosis). However, in many cases the duplicated regions are on different chromosomes, implying that either there was originally a tandem duplication followed by a translocation of one copy to a new site or that the duplication arose by some different mechanism altogether. The extreme case of a segmental duplication is when an entire genome is duplicated, in which case the diploid genome initially becomes tetraploid. As the duplicated copies evolve differences from one another, the genome can gradually become effectively a diploid again, although homologies between the diverged copies leave evidence of the event. This is especially common in plant genomes. The present state of analysis of the human genome identifies many individual duplicated regions, and there is evidence for a whole-genome duplication in the vertebrate lineage .
One curious feature of the human genome is the presence of sequences that do not appear to have coding functions but that nonetheless show an evolutionary conservation higher than the background level. As detected by comparison with other genomes (e.g., the mouse genome), these represent about 5% of the total genome. Are these sequences associated with protein-coding sequences in some functional way? Their density on chromosome 18 is the same as elsewhere in the genome, although chromosome 18 has a significantly lower concentration of protein-coding genes. This suggests indirectly that their function is not connected with structure or expression of protein-coding genes.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


