


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 11-12-2020
Date: 21-1-2021
Date: 21-12-2020
|
The Biological Reaction of Biosensor
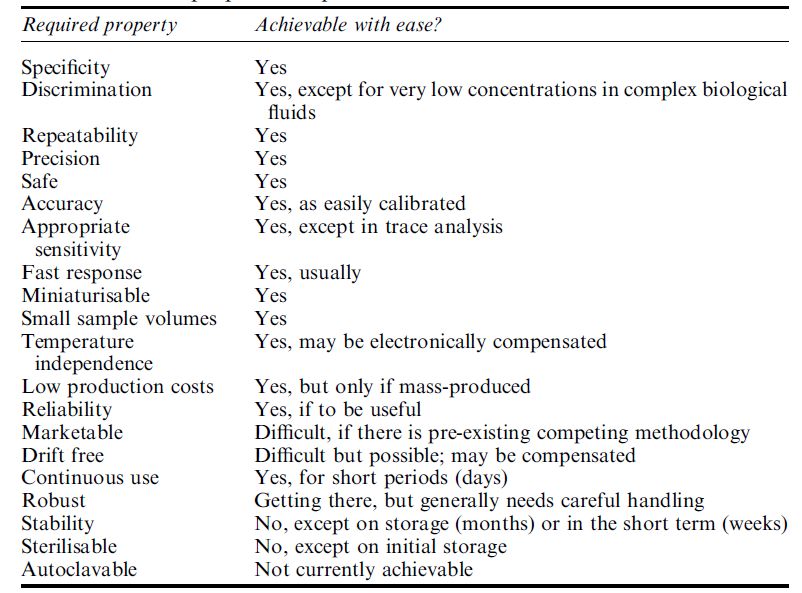
An important factor in most biosensor configurations is the sensing surface. This normally consists of a thin layer of biologically active material in intimate contact with the electronic or optical transducer. In some cases the biological material may be covalently or non-covalently attached to the surface, but often in electrochemical biosensors it forms part of a thin membrane covering the sensing surface. Generally, the conversion of the biological process into an electronic or optical signal is most efficient where there is minimal distance between where the biological reaction or binding takes place and where the electronic transduction takes place.
In addition, it is important for the retention of biological activity that the biological material is not lost into analyte solutions. The immobilisation technology for holding the biocatalyst in place is extensive, with examples of immobilisation methods summarised in Table . Much current research is directed at stabilising enzymes for use in biosensors. At a suitable pH, polyelectrolytes such as diethylaminoethyldextran wrap around enzymes, restricting their movement and reducing their tendency to denature. Polyelectrolytes in combination with polyalcohols, such as sorbitol and lactitol, have been shown to stabilise enzymes considerably against thermal inactivation for use in biosensors. More recently, enzymes have been specifically engineered for their use in biosensors.
Table . Examples of biosensor immobilisation methods.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|