


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 9-12-2020
Date: 30-11-2015
Date: 27-2-2021
|
Line Probe Assays
In line probe assays (Figure 1), capture probes are printed in parallel bands (lines) on a membrane. Line probe assays have been developed to distinguish strains or genotypes of infectious agents. Each band or lane contains capture probes that differ only in nucleotides that are characteristic for each strain or genotype. The target nucleic acid is typically first amplified by PCR utilizing biotin-labelled primers before addition to the line probe membrane in a hybridisation buffer. Following a wash, a streptavidin-enzyme conjugate is added and allowed to bind to biotin. Following another wash a colourless substrate is added and will be changed by the enzyme to a precipitable coloured product. The line or band corresponding to one specific genotype will then become coloured (Figure 1).
Commercial line probe assays are used for the detection of genotypes of HPV and hepatitis C virus (HCV), strains of atypical mycobacteria and for detection of HTLV-1 (human T-cell lymphotropic virus).
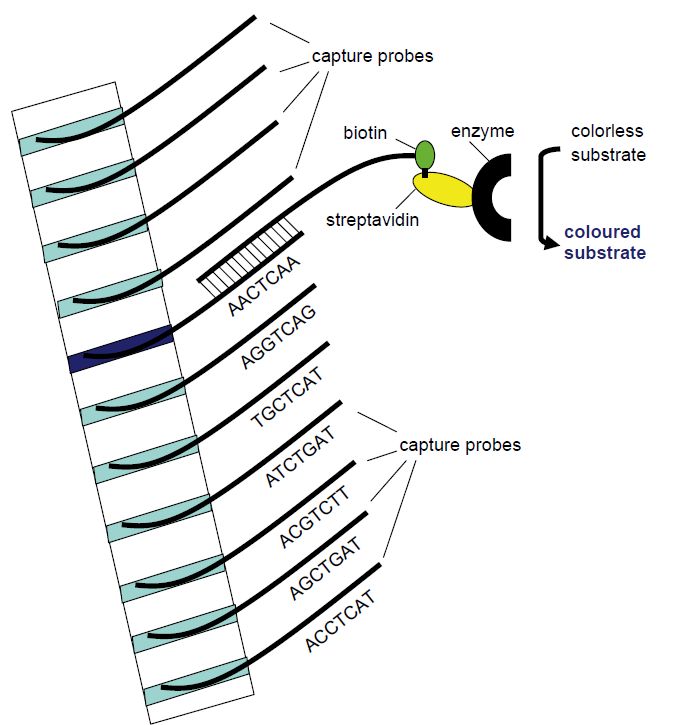
Figure 1: Principle of the line probe assay. Different capture probe sequences are fixed in different bands in a membrane strip. The amplification product will hybridise with the capture probe of complementary sequence. Utilising biotin-labelled PCR primers, the position of the complementary capture probe can be visualised as a coloured band following addition of streptavidin-bound enzyme that will change a non-coloured substrate to a coloured product that precipitates in the band.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أولياء أمور الطلبة يشيدون بمبادرة العتبة العباسية بتكريم الأوائل في المراحل المنتهية
|
|
|