

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Dihydroxylation of alkenes
المؤلف:
University of Missouri System
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry ii
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
7-10-2020
2393
Dihydroxylation of alkenes
Alkenes are oxidized to cis-1,2-diols by osmium tetroxide (OsO4). The stereospecificity is due to the formation of a cyclic osmate ester intermediate. Osmium tetroxide can be used directly, but it is normally used in catalytic amounts, and is regenerated by N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide.

Examples
Questions:
1. Give the major product.
.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=131&height=51#fixme)
2. What is the product in the dihydroxylation of (Z)-3-hexene?

3. What is the product in the dihydroxylation of (E)-3-hexene?
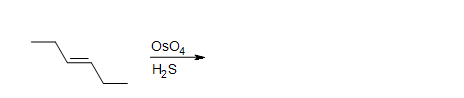
4. Draw the intermediate of this reaction.
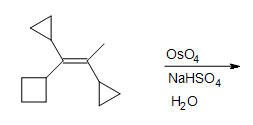
5. Fill in the missing reactants, reagents, and product.
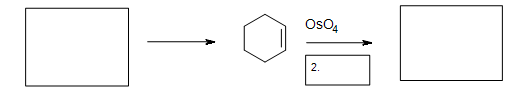
Solutions
1. A syn-1,2-ethanediol is formed. There is no stereocenter in this particular reaction. The OH groups are on the same side.
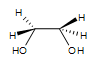
2. Meso-3,4-hexanediol is formed. There are 2 stereocenters in this reaction.
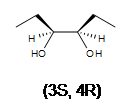
3. A racemic mixture of 3,4-hexanediol is formed. There are 2 stereocenters in both products.
4. A cyclic osmic ester is formed.
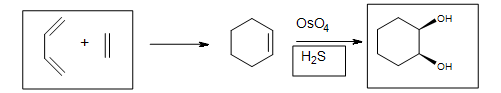
5. The Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction is needed in the first box to form the cyclohexene. The second box needs a reagent to reduce the intermediate cyclic ester. The third box has the product: 1,2-cyclohexanediol.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















