
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Refractors: Objectives
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 250
19-8-2020
1796
Refractors: Objectives
The lens-maker’s formula expresses the focal length, F, of a lens in terms of the refractive index, n, of the material (usually glass) and the radii of curvature, r1, r2, of the two lens’ surfaces. It can be expressed conveniently in the form
 (1)
(1)
(In this form, values of r are positive when light rays meet a convex curvature and are negative when they meet a concave curvature.) Thus, in general, if r1 is positive and r2 is negative, a simple lens has a positive, real focus. A beam of parallel light which falls on the lens is, therefore. By applying this lens to a beam of light from a star which can be considered to be at infinity, an image of the star will be formed at the focus of the lens. This image is available for viewing with an eyepiece or for recording on a detector. The lens acts as light-collector and image-former. When it is used in this way in a telescope system it is commonly known as the objective.
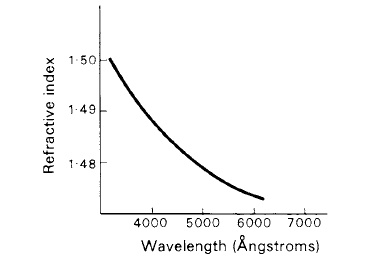
Figure 1. The dispersion curve of a typical crown glass.
A single-lens objective is unsatisfactory for astronomical purposes as the images produced suffer from defects or aberrations of different kinds. Considerable effort has been applied to the design of objectives to remove or reduce the aberrations and refractor telescopes show a variety of construction depending on their intended function and the way particular aberrations have been compensated. Telescope objectives may suffer from the following defects:
(i) chromatic aberration,
(ii) spherical aberration,
(iii) coma,
(iv) astigmatism,
(v) curvature of field,
(vi) distortion of field,
and each of these effects is discussed in the following subsections.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















