
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Atmospheric refraction: The laws of refraction
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 112
30-7-2020
1929
Atmospheric refraction: The laws of refraction
When a ray of light passes from a transparent substance of one density into another transparent substance of a different density, the ray changes direction. It is said to be refracted and the amount of the deviation from its original direction depends upon the relative densities of the substances.
Let a ray of light, AB, passing through a vacuum, meet the upper boundary PQ of a plane parallel slab of glass at an angle i to the normal BN to the slab (figure 1). The angle NBA is called the angle of incidence. The ray is refracted upon entering the slab so that it leaves the lower boundary RS of the slab at C. Angle MBC, or r , is called the angle of refraction and is less than i . The ray’s path on leaving at the point C is along the line CD, at an angle ZCD to the normal ZC.
Then the first law of refraction states that the incident ray AB, the normal BN and the refracted
ray BC are coplanar.
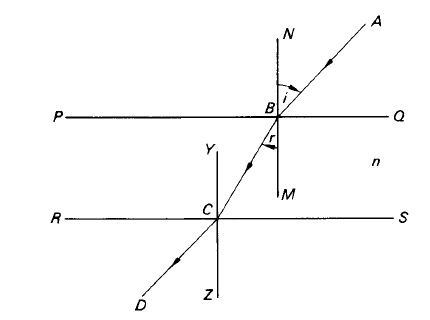
Figure1. Refraction of a light beam by a slab.
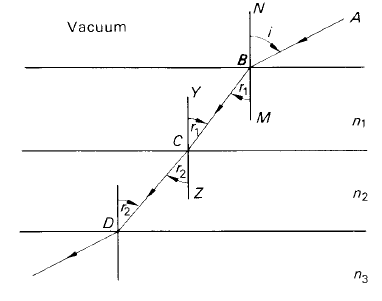
Figure 2. Refraction by a series of slabs.
The second law (Snell’s law) states that
sin i/sin r = n (1)
where n is called the index of refraction of the substance making up the slab. Since r < i, n > 1 .
If YCZ is the normal at C, ∠YCB = ∠MBC = r (PQ being parallel to RS) and hence, since ray paths are reversible, ∠ZCD = i . In other words, the emergent ray CD will be parallel to AB but not collinear with it.
For a number of plane, parallel slabs of indices of refraction n1, n2, n3, . . . , n j , we can extend relation (1). In figure 2, the ray of light passes from slab 1, of refractive index n1, into slab 2, of refractive index n2. Then by Snell’s law,
sin i = n1 sin r1.
Also, for the second slab,
sin i = n2 sin r2.
Hence, for j slabs, we have
sin i = n1 sin r1 = n2 sin r2 = n3 sin r3 = · · · = n j sin r j . (2)

Figure 3. Refraction by the Earth’s atmosphere of light from a star.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















