

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Sublimation and Deposition
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
30-4-2020
1433
Sublimation and Deposition
Some solids can transition directly into the gaseous state, bypassing the liquid state, via a process known as sublimation. At room temperature and standard pressure, a piece of dry ice (solid CO2) sublimes, appearing to gradually disappear without ever forming any liquid. Snow and ice sublime at temperatures below the melting point of water, a slow process that may be accelerated by winds and the reduced atmospheric pressures at high altitudes. When solid iodine is warmed, the solid sublimes and a vivid purple vapor forms (Figure1.1). The reverse of sublimation is called deposition, a process in which gaseous substances condense directly into the solid state, bypassing the liquid state. The formation of frost is an example of deposition.

Figure1.1 : Sublimation of solid iodine in the bottom of the tube produces a purple gas that subsequently deposits as solid iodine on the colder part of the tube above. (credit: modification of work by Mark Ott)
Like vaporization, the process of sublimation requires an input of energy to overcome intermolecular attractions. The enthalpy of sublimation, ΔHsub, is the energy required to convert one mole of a substance from the solid to the gaseous state. For example, the sublimation of carbon dioxide is represented by:
Likewise, the enthalpy change for the reverse process of deposition is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to that for sublimation:
Consider the extent to which intermolecular attractions must be overcome to achieve a given phase transition. Converting a solid into a liquid requires that these attractions be only partially overcome; transition to the gaseous state requires that they be completely overcome. As a result, the enthalpy of fusion for a substance is less than its enthalpy of vaporization. This same logic can be used to derive an approximate relation between the enthalpies of all phase changes for a given substance. Though not an entirely accurate description, sublimation may be conveniently modeled as a sequential two-step process of melting followed by vaporization in order to apply Hess’s Law.
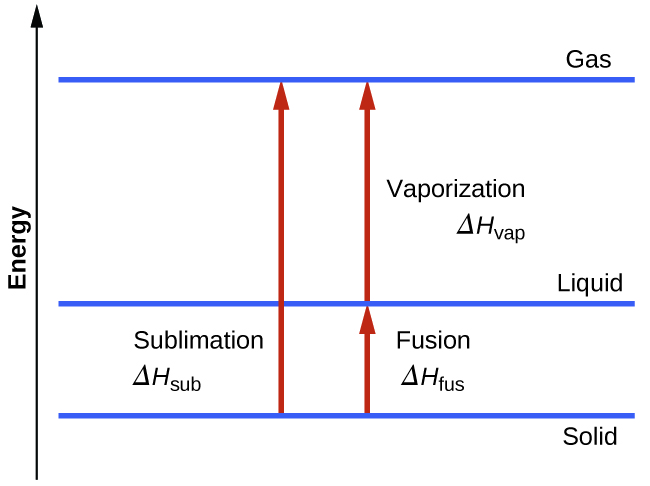
Figure 1.2 : For a given substance, the sum of its enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization is approximately equal to its enthalpy of sublimation.
 الاكثر قراءة في اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















