


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 25-12-2019
Date: 23-12-2019
Date: 17-8-2018
|
Step 1 - Claisen Condensation
An early step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other ‘isoprenoid’ compounds is a Claisen condensation between two acetyl CoA molecules. An initial trans-thioesterase process transfers the acetyl group of the first acetyl CoA to an enzymatic cysteine (Reaction 1). In the Claisen condensation phase of the reaction, the alpha-carbon of a second acetyl CoA is deprotonated, forming an enolate (Reaction 2).

The enolate carbon attacks the electrophilic thioester carbon, forming a tetrahedral intermediate (Reaction 3) which quickly collapses to expel the cysteine thiol (Reaction 4) and produce acetoacetyl CoA.
Step 2 - Aldol Condensation
Acetyl CoA then reacts with the acetoacetyl CoA in an aldol-like addition. Subsequent hydrolysis produces (3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA).
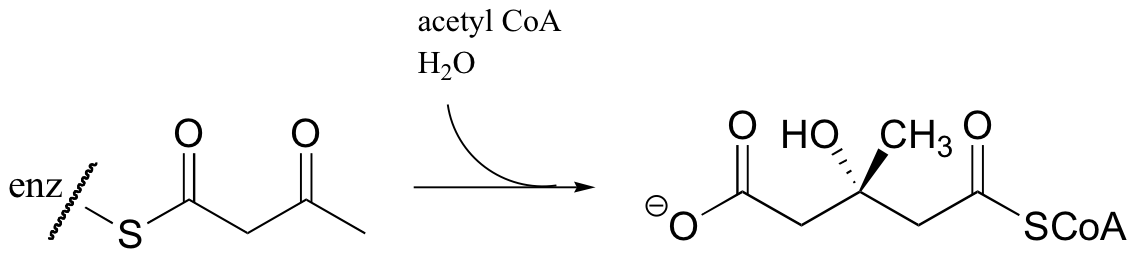
Generating HMG-CoA
Step 3 - Reduction of the Thioester
The thioester is reduced first to an aldehyde, then to a primary alcohol by two equivalents of NADPH producing (R)-mevalonate. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is the target of the statin family of cholesterol-lowering drugs.
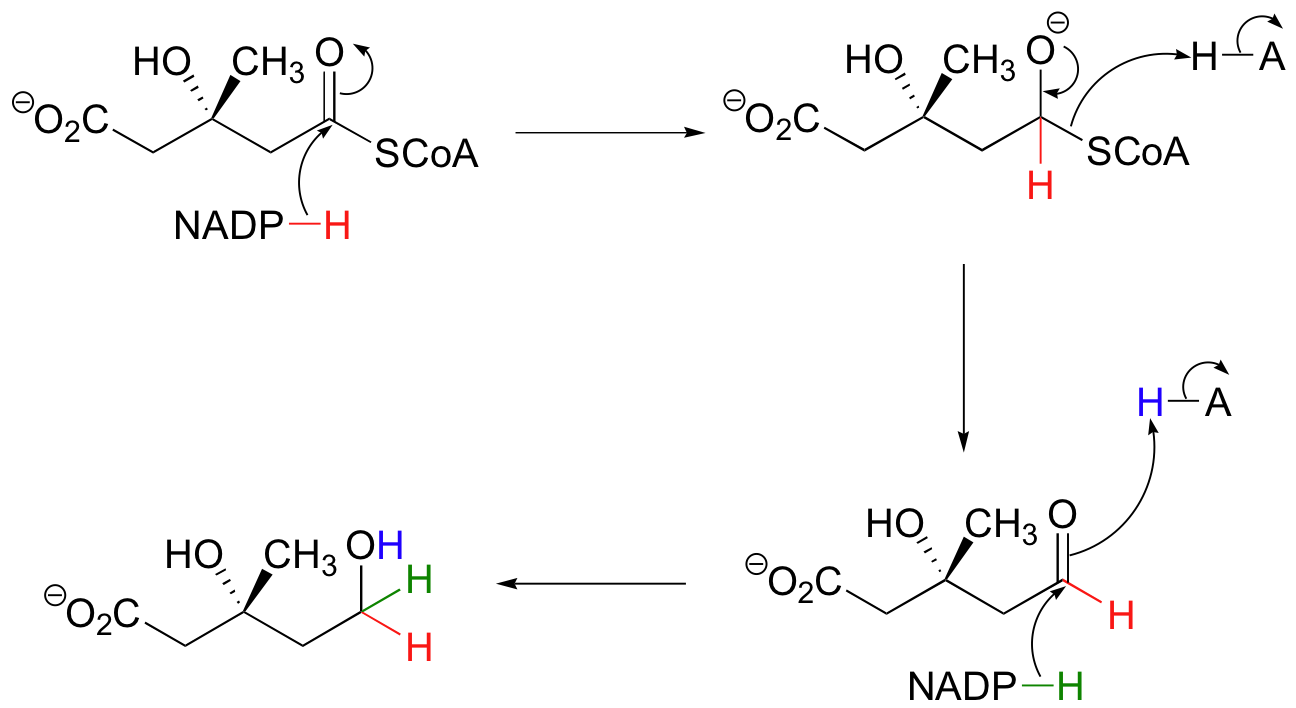
Generating (R)-Mevalonate
Step 4 - Mevalonate Phosphorylation
Two phsophorylations by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) occur at the terminal hydroxyl/phosphorus group through nucleophilic substitution, followed by a third ATP phosphorylation of the tertiary hydroxyl group.
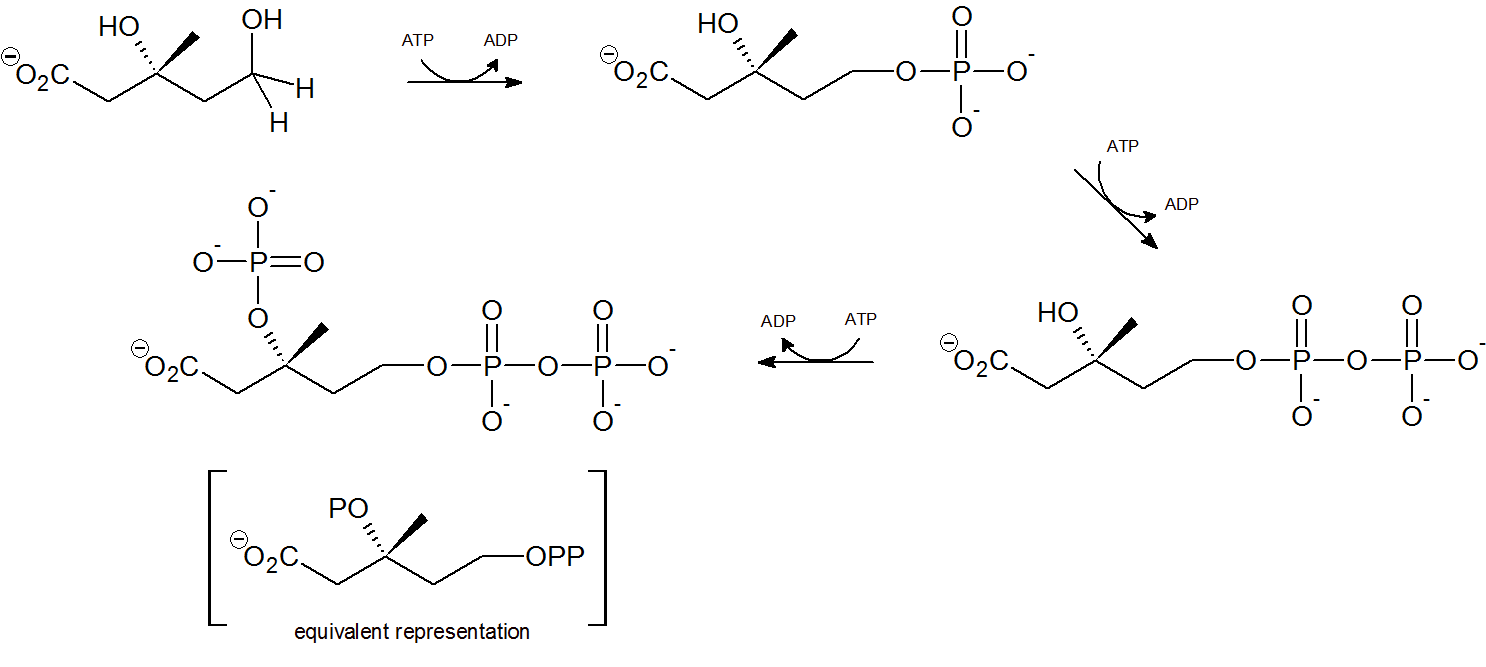
Step 5 - Decarboxylation
Finally isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP), the 'building block' for all isoprenoid compounds, is formed from a decarboxylation-elimination reaction.
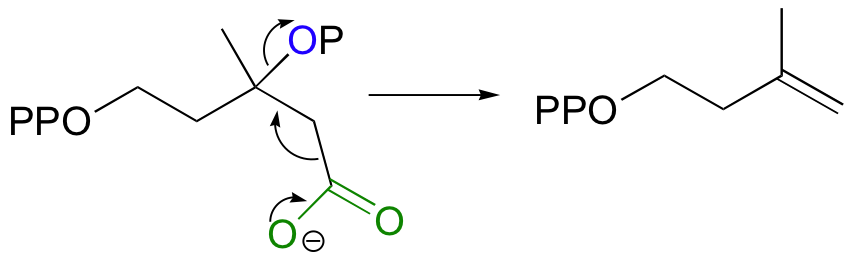



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|