

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Crown Ethers
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
24-10-2019
1705
Crown Ethers
It is possible to dissolve ionic compounds in organic solvents using crown ethers. Cyclic polyether with four or more oxygen atoms separated by two or three carbon atoms. All crown ethers have a central cavity that can accommodate a metal ion coordinated to the ring of oxygen atoms., cyclic compounds with the general formula (OCH2CH2)n. Crown ethers are named using both the total number of atoms in the ring and the number of oxygen atoms. Thus 18-crown-6 is an 18-membered ring with six oxygen atoms (part (a) in Figure 1.1 ). The cavity in the center of the crown ether molecule is lined with oxygen atoms and is large enough to be occupied by a cation, such as K+. The cation is stabilized by interacting with lone pairs of electrons on the surrounding oxygen atoms. Thus crown ethers solvate cations inside a hydrophilic cavity, whereas the outer shell, consisting of C–H bonds, is hydrophobic. Crown ethers are useful for dissolving ionic substances such as KMnO4 in organic solvents such as isopropanol [(CH3)2CHOH] (Figure 1.1). The availability of crown ethers with cavities of different sizes allows specific cations to be solvated with a high degree of selectivity.
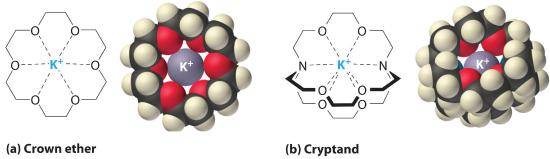
Figure 1.1: Crown Ethers and Cryptands (a) The potassium complex of the crown ether 18-crown-6. Note how the cation is nestled within the central cavity of the molecule and interacts with lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atoms. (b) The potassium complex of 2,2,2-cryptand, showing how the cation is almost hidden by the cryptand. Cryptands solvate cations via lone pairs of electrons on both oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
Cryptands (from the Greek kryptós, meaning “hidden”) are compounds that can completely surround a cation with lone pairs of electrons on oxygen and nitrogen atoms (Figure 1.1b). The number in the name of the cryptand is the number of oxygen atoms in each strand of the molecule. Like crown ethers, cryptands can be used to prepare solutions of ionic compounds in solvents that are otherwise too nonpolar to dissolve them.
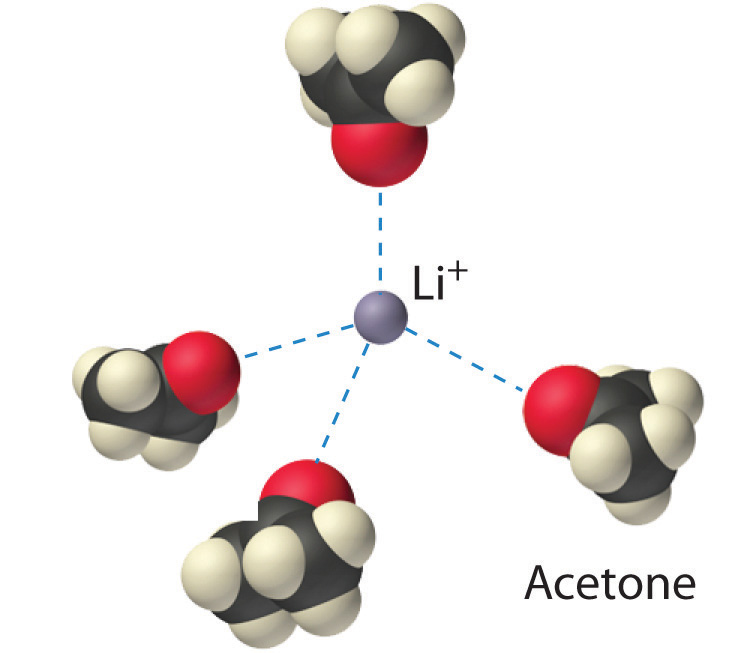
Figure 1.3: Ion–Dipole Interactions in the Solvation of Li+ Ions by Acetone, a Polar Solvent
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















