

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Carboxylic Acids, RCO2H
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
14-10-2019
1889
Carboxylic Acids, RCO2H
The IUPAC system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix to these classes. The –e ending is removed from the name of the parent chain and is replaced -anoic acid. Since a carboxylic acid group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain, it is always is given the #1 location position in numbering and it is not necessary to include it in the name.
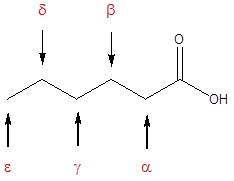
Many carboxylic acids are called by the common names. These names were chosen by chemists to usually describe a source of where the compound is found. In common names of aldehydes, carbon atoms near the carboxyl group are often designated by Greek letters. The atom adjacent to the carbonyl function is alpha, the next removed is beta and so on.
| Formula | Common Name | Source | IUPAC Name | Melting Point | Boiling Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCO2H | formic acid | ants (L. formica) | methanoic acid | 8.4 ºC | 101 ºC |
| CH3CO2H | acetic acid | vinegar (L. acetum) | ethanoic acid | 16.6 ºC | 118 ºC |
| CH3CH2CO2H | propionic acid | milk (Gk. protus prion) | propanoic acid | -20.8 ºC | 141 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)2CO2H | butyric acid | butter (L. butyrum) | butanoic acid | -5.5 ºC | 164 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)3CO2H | valeric acid | valerian root | pentanoic acid | -34.5 ºC | 186 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)4CO2H | caproic acid | goats (L. caper) | hexanoic acid | -4.0 ºC | 205 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)5CO2H | enanthic acid | vines (Gk. oenanthe) | heptanoic acid | -7.5 ºC | 223 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)6CO2H | caprylic acid | goats (L. caper) | octanoic acid | 16.3 ºC | 239 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)7CO2H | pelargonic acid | pelargonium (an herb) | nonanoic acid | 12.0 ºC | 253 ºC |
| CH3(CH2)8CO2H | capric acid | goats (L. caper) | decanoic acid | 31.0 ºC | 219 ºC |
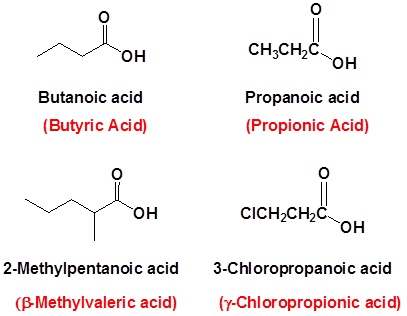
Example (Common Names Are in Red)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















