

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Connection Between SN1 and E1
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
3-8-2019
1548
The Connection Between SN1 and E1
The E1 mechanism is nearly identical to the SN1 mechanism, differing only in the course of reaction taken by the carbocation intermediate. As shown by the following equations, a carbocation bearing beta-hydrogens may function either as a Lewis acid (electrophile), as it does in the SN1 reaction, or a Brønsted acid, as in the E1 reaction.
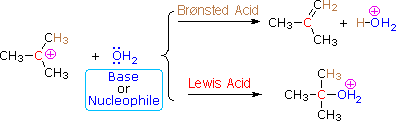
Thus, hydrolysis of tert-butyl chloride in a mixed solvent of water and acetonitrile gives a mixture of 2-methyl-2-propanol (60%) and 2-methylpropene (40%) at a rate independent of the water concentration. The alcohol is the product of an SN1 reaction and the alkene is the product of the E1 reaction. The characteristics of these two reaction mechanisms are similar, as expected. They both show first order kinetics; neither is much influenced by a change in the nucleophile/base; and both are relatively non-stereospecific.
(CH3)3C–Cl + H2O ——> [ (CH3)3C(+) ] + Cl(–) + H2O ——> (CH3)3C–OH + (CH3)2C=CH2 + HCl + H2O
To summarize, when carbocation intermediates are formed one can expect them to react further by one or more of the following modes:
- The cation may bond to a nucleophile to give a substitution product.
- The cation may transfer a beta-proton to a base, giving an alkene product.
- The cation may rearrange to a more stable carbocation, and then react by mode #1 or #2.
Since the SN1 and E1 reactions proceed via the same carbocation intermediate, the product ratios are difficult to control and both substitution and elimination usually take place.
Having discussed the many factors that influence nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions of alkyl halides, we must now consider the practical problem of predicting the most likely outcome when a given alkyl halide is reacted with a given nucleophile. As we noted earlier, several variables must be considered, the most important being the structure of the alkyl group and the nature of the nucleophilic reactant. The nature of the halogen substituent on the alkyl halide is usually not very significant if it is Cl, Br or I. In cases where both SN2 and E2 reactions compete, chlorides generally give more elimination than do iodides, since the greater electronegativity of chlorine increases the acidity of beta-hydrogens. Indeed, although alkyl fluorides are relatively unreactive, when reactions with basic nucleophiles are forced, elimination occurs (note the high electronegativity of fluorine).
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















