
The E2 Reaction and the Deuterium Isotope Effect
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 2-8-2019
2-8-2019
 1670
1670
The E2 Reaction and the Deuterium Isotope Effect
E2, bimolecular elimination, was proposed in the 1920s by British chemist Christopher Kelk Ingold. Unlike E1 reactions, E2 reactions remove two subsituents with the addition of a strong base, resulting in an alkene.
An E2 reaction is a bimolecular elimination reaction; thus, two molecules are involved in the rate-limiting step. In this section, we are concerned with E2 reactions involving an alkyl halide and a base.
Use molecular models to assist you to understand the difference between syn periplanar and anti periplanar, and to appreciate why E2 eliminations are stereospecific.
Note that when deuterium is used the kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is referred to as the deuterium isotope effect. A C–H
bond is about 5 kJ/mol weaker than a C–D bond. So if the rate-limiting step involves a breaking of this bond as it does at the E2 transition state there will be a substantial difference in reaction rates when comparing deuterated and non-deuterated analogues. Indeed, the reaction of 2-bromopropane with sodium ethoxide (NaOEt) is 6.7 times faster than its deuterated counterpart, providing evidence consistent with an E2 mechanism.
E2 reactions are typically seen with secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, but a hindered base is necessary with a primary halide. The mechanism by which it occurs is a single step concerted reaction with one transition state. The rate at which this mechanism occurs is second order kinetics, and depends on both the base and alkyl halide. A good leaving group is required because it is involved in the rate determining step. The leaving groups must be coplanar in order to form a pi bond; carbons go from sp3 to sp2 hybridization states.
To get a clearer picture of the interplay of these factors involved in a a reaction between a nucleophile/base and an alkyl halide, consider the reaction of a 2º-alkyl halide, isopropyl bromide, with two different nucleophiles. In one pathway, a methanethiolate nucleophile substitutes for bromine in an SN2 reaction. In the other (bottom) pathway, methoxide ion acts as a base (rather than as a nucleophile) in an elimination reaction. As we will soon see, the mechanism of this reaction is single-step, and is referred to as the E2 mechanism.
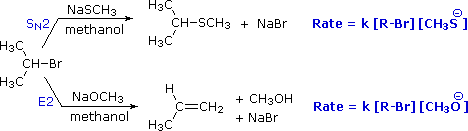
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


