

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Stereogenic Nitrogen
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
8-7-2019
2037
Stereogenic Nitrogen
Single-bonded nitrogen is pyramidal in shape, with the non-bonding electron pair pointing to the unoccupied corner of a tetrahedral region. Since the nitrogen in these compounds is bonded to three different groups, its configuration is chiral. The non-identical mirror-image configurations are illustrated in the following diagram (the remainder of the molecule is represented by R, and the electron pair is colored yellow). If these configurations were stable, there would be four additional stereoisomers of ephedrine and pseudoephedrine. However, pyramidal nitrogen is normally not configurationally stable. It rapidly inverts its configuration (equilibrium arrows) by passing through a planar, sp2-hybridized transition state, leading to a mixture of interconverting R and S configurations. If the nitrogen atom were the only chiral center in the molecule, a 50:50 (racemic) mixture of R and S configurations would exist at equilibrium. If other chiral centers are present, as in the ephedrin isomers, a mixture of diastereomers will result. The take-home message is that nitrogen does not contribute to isolable stereoisomers.
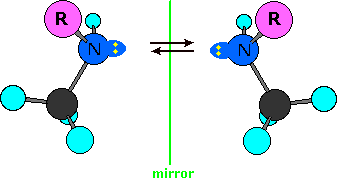
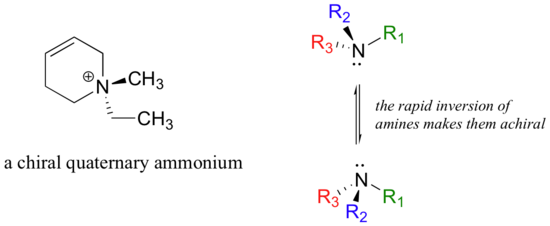
Asymmetric quaternary ammonium groups are also chiral. Amines, however, are not chiral, because they rapidly invert, or turn ‘inside out’, at room temperature.
The phosphorus center of phosphate ion and organic phosphate esters, for example, is tetrahedral, and thus is potentially a stereocenter.

We will see in chapter 10 how researchers, in order to investigate the stereochemistry of reactions at the phosphate center, incorporated sulfur and/or 17O and 18O isotopes of oxygen (the ‘normal’ isotope is 16O) to create chiral phosphate groups. Phosphate triesters are chiral if the three substituent groups are different.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















