

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Cytochromes
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
24-6-2019
1810
Cytochromes
The cytochromes (from the Greek cytos, meaning “cell”, and chroma, meaning “color”) were first identified in the 1920s by spectroscopic studies of cell extracts. Based on the wavelength of the maximum absorption in the visible spectrum, they were classified as cytochromes a (with the longest wavelength), cytochromes b (intermediate wavelength), and cytochromes c (shortest wavelength). It quickly became apparent that there was a correlation between their spectroscopic properties and other physical properties. For examples, cytochromes c are generally small, soluble proteins with a reduction potential of about +0.25 V, whereas cytochromes b are larger, less-soluble proteins with reduction potentials of about 0 V.
All cytochromes contain iron, and the iron atom in all cytochromes is coordinated by a planar array of four nitrogen atoms provided by a cyclic tetradentate ligand called a porphyrin. The iron–porphyrin unit is called a heme group. The structures of a typical porphyrin (protoporphyrin IX) and its iron complex (protoheme) are shown here. In addition to the four nitrogen atoms of the porphyrin, the iron in a cytochrome is usually bonded to two additional ligands provided by the protein, as shown in Figure 1.1.
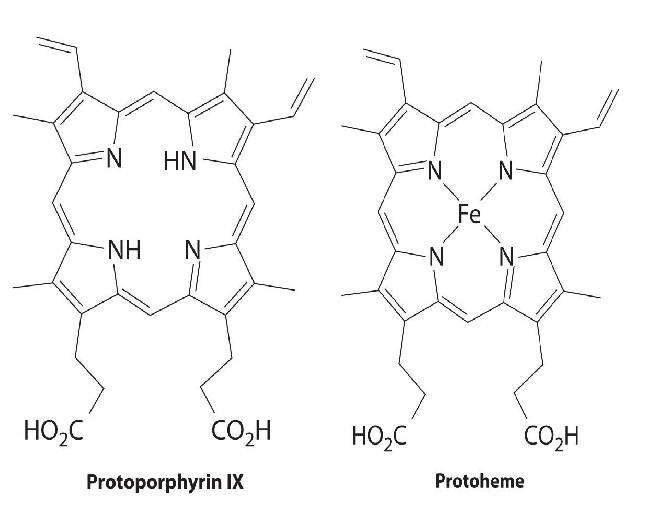
A cytochrome. Shown here is protoporphyrin IX and its iron complex, protoheme.

Figure 1.1 : A Cytochrome c. In a cytochrome c, the heme iron is coordinated to the nitrogen atom of a histidine imidazole and the sulfur atom of a methionine thioether, in addition to the four nitrogen atoms provided by the porphyrin.
In contrast to the blue copper proteins, two electron configurations are possible for both the oxidized and reduced forms of a cytochrome, and this has significant structural consequences. Thus Fe2+ is d6 and can be either high spin (with four unpaired electrons) or low spin (with no unpaired electrons). Similarly, Fe3+ is d5 and can also be high spin (with five unpaired electrons) or low spin (with one unpaired electron). In low-spin heme complexes, both the Fe2+ and the Fe3+ ions are small enough to fit into the “hole” in the center of the porphyrin; hence the iron atom lies almost exactly in the plane of the four porphyrin nitrogen atoms in both cases. Because cytochromes b and c are low spin in both their oxidized and reduced forms, the structures of the oxidized and reduced cytochromes are essentially identical. Hence minimal structural changes occur after oxidation or reduction, which makes electron transfer to or from the heme very rapid.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















