


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 24-4-2019
Date: 15-2-2019
Date: 17-4-2019
|
The compound NiTi, popularly known as “memory metal” or nitinol (nickel–titanium Naval Ordinance Laboratory, after the site where it was first prepared), illustrates the importance of deformations. If a straight piece of NiTi wire is wound into a spiral, it will remain in the spiral shape indefinitely, unless it is warmed to 50°C–60°C, at which point it will spontaneously straighten out again. The chemistry behind the temperature-induced change in shape is moderately complex, but for our purposes it is sufficient to know that NiTi can exist in two different solid phases.
The high-temperature phase has the cubic cesium chloride structure, in which a Ti atom is embedded in the center of a cube of Ni atoms (or vice versa). The low-temperature phase has a related but kinked structure, in which one of the angles of the unit cell is no longer 90°. Bending an object made of the low-temperature (kinked) phase creates defects that change the pattern of kinks within the structure. If the object is heated to a temperature greater than about 50°C, the material undergoes a transition to the cubic high-temperature phase, causing the object to return to its original shape. The shape of the object above 50°C is controlled by a complex set of defects and dislocations that can be relaxed or changed only by the thermal motion of the atoms.
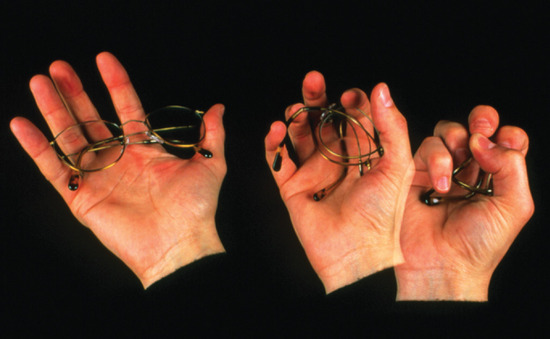
Memory metal. Flexon is a fatigue-resistant alloy of Ti and Ni that is used as a frame for glasses because of its durability and corrosion resistance.
Memory metal has many other practical applications, such as its use in temperature-sensitive springs that open and close valves in the automatic transmissions of cars. Because NiTi can also undergo pressure- or tension-induced phase transitions, it is used to make wires for straightening teeth in orthodontic braces and in surgical staples that change shape at body temperature to hold broken bones together
Another flexible, fatigue-resistant alloy composed of titanium and nickel is Flexon. Originally discovered by metallurgists who were creating titanium-based alloys for use in missile heat shields, Flexon is now used as a durable, corrosion-resistant frame for glasses, among other uses.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|