

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The structure of carbon dioxide
المؤلف:
........
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
............
1-4-2019
2153
The structure of carbon dioxide
The fact that carbon dioxide is a gas indicates that it consists of small, simple molecules. Carbon can form these molecules because it can form double bonds with oxygen.
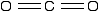
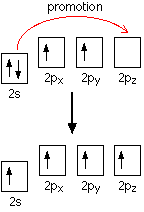
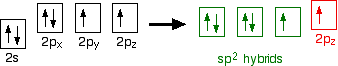
None of the other elements in Group 4 form double bonds with oxygen, so their oxides adopt completely different structures. When carbon forms bonds with oxygen, it promotes one of its 2s electrons into the empty 2p level. This produces 4 unpaired electrons.
These electrons are rearranged by hybridizing the 2s electron and one of the 2p electrons to make two sp1 hybrid orbitals of equal energy. The other 2p electrons are unaffected during this process.
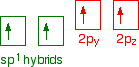
The figure below illustrates this:
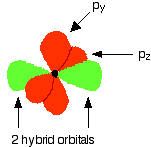
Notice that the two green lobes are two different hybrid orbitals, arranged as far from each other as possible (although the two hybrid orbitals have an arrangement similar to a p orbital, it is important not to confuse the two).
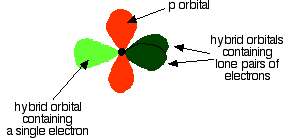
Oxygen's electronic structure is 1s22s22px22py12pz1, and its orbitals must also hybridize. In this case, sp2 hybrids are formed from the s orbital and two of the p orbitals, rearranging to form 3 orbitals of equal energy, leaving a temporarily unaffected p orbital.
As shown below, two of the sp2 hybrid orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons.
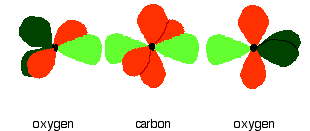
In the figure below, the carbon and oxygen atoms are arranged in pre-bonding position:
The green hybrid orbitals overlap end-to-end, forming covalent bonds. These are called sigma bonds, and are shown as orange in the next diagram. The sigma bonding brings the p orbitals close enough to overlap.
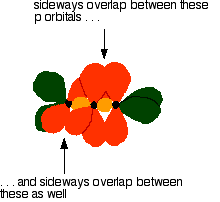
This overlap between the two sets of p orbitals produces two pi
bonds, similar to the pi bond found in ethene. These pi
bonds are twisted at 90° to each other in the final molecule.
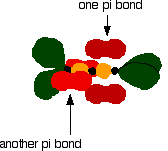
To form a carbon-oxygen double bond, it is necessary for the lobes of the p orbitals on the carbon and the oxygen to overlap correctly.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















