


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 13-10-2020
Date: 31-7-2019
Date: 18-11-2019
|
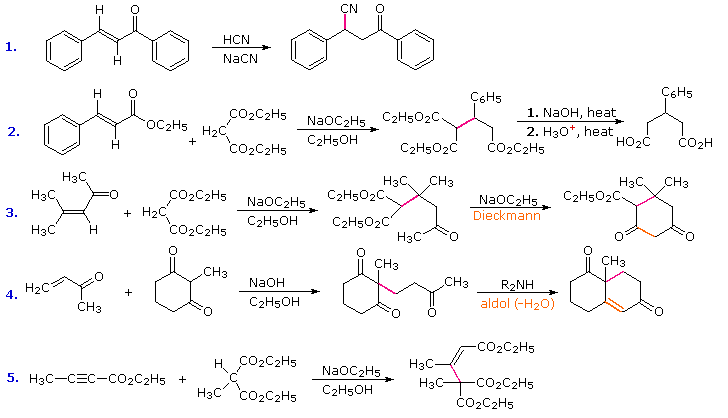
Conjugative addition of carbon nucleophiles to unsaturated esters, ketones, nitriles, sulfones and other activated double bonds is a useful synthetic method known as the Michael reaction. In combination with alkylations and condensations, the Michael reaction may be used to construct a wide variety of complex molecules from relatively simple starting materials. The carbon nucleophiles used in the following examples include cyanide ion, sodium diethylmalonate and the conjugate base of cyclohexane-1,3-dione. These anions are sufficiently stable that their addition reactions may be presumed reversible. If this is so, the thermodynamic argument used for hetero-nucleophile additions would apply here as well, and would indicate preferential formation of 1,4-addition products. Cyanide addition does not always follow this rule, and aldehydes often give 1,2-products (cyanohydrins). In each case the initial reaction is a Michael addition, and the new carbon-carbon bond is colored magenta. Any subsequent bonds that are formed by other reactions are colored orange.




|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي يقيم ورشة تطويرية ودورة قرآنية في النجف والديوانية
|
|
|