

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Reactions of Free Radicals : Intermolecular Addition Reactions
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
28-8-2018
3067
Reactions of Free Radicals : Intermolecular Addition Reactions
Addition reactions to carbon:carbon double bonds are among the most important free radical reactions employed by chemists. The anti-Markovnikov addition of HBr to alkenes is one such reaction, and the peroxide initiated addition of carbon tetrachloride to 1-hexene is another. As the following equations demonstrate, radical addition to a substituted double bond is regiospecific (i.e. the more stable product radical is preferentially formed in the chain addition process).
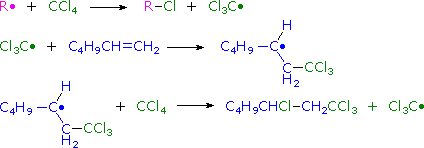
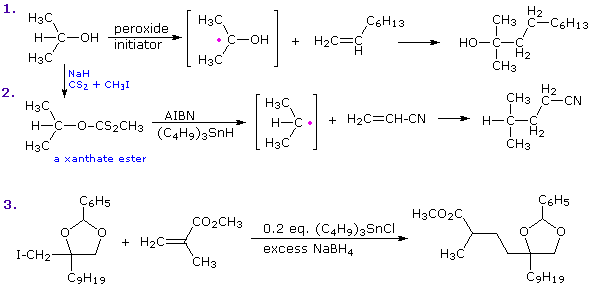
The following diagram provides other examples of radical addition to double bonds. The first two equations show how different radicals may be generated selectively from the same compound. Although 2-propanol has three different groups of hydrogen, simple atom abstraction by an oxy radical occurs exclusively at the 3º-carbon bonded to oxygen. By using the xanthate derivative, the carbon-oxygen bond may be homolytically cleaved to form the isopropyl radical. Double bond conjugated with carbonyl or nitrile functions are particularly good radical acceptors, as shown in the last two examples.
If a radical transfer reagent, such as an alkyl halide or xanthate, is not present in excess, an alkene derived radical may exist long enough to add to other alkene molecules in a repetitive fashion, leading to a polymeric product, as shown here. The new C–C bond(s) are colored magenta.
~~CH2CHR• + CH2=CHR –––> ~~CH2CHR–CH2CHR• + CH2=CHR –––> ~~CH2CHR–CH2CHR–CH2CHR•
Indeed, free radical polymerization of simple substituted alkenes is so facile that bulk quantities of these compounds must be protected by small amounts of radical inhibitors during storage. These inhibitors, or radical scavengers, may themselves be radicals (e.g. oxygen and galvinoxyl) or compounds that react rapidly with propagating radicals to produce stable radical species that terminate the chain. Inhibitors include quinones, substituted phenols, aryl amines and nitro compounds.
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















