

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
An Example of Extensive Spin-Splitting
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
13-8-2018
2064
An Example of Extensive Spin-Splitting
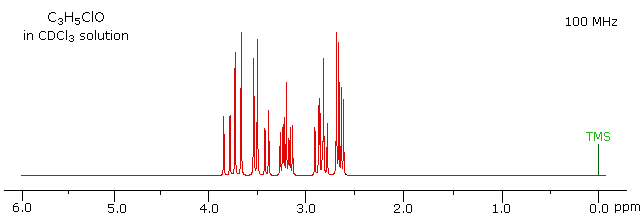
Not all simple compounds have simple proton nmr spectra. The following example not only illustrates this point, but also demonstrates how a careful structural analysis can rationalize an initially complex spectrum.
The 100 MHz 1H nmr spectrum of a C3H5ClO compound is initially displayed. This spectrum is obviously complex and not easily interpreted, except for concluding that no olefinic C-H protons are present. By clicking the "500 MHz Spectrum" button beneath the spectrum, a higher field spectrum will appear. Here it is clear that each of the five hydrogen atoms in the molecule is structurally unique, and is producing a separate signal. Also, it is clear there is considerable spin coupling of all the hydrogens. To see the coupling patterns more clearly it is necessary to expand and enhance the spectrum in these regions. For purposes of our demonstration, this can be done by clicking on any one of the signal multiplets. Clicking in an open area should return the original 500 MHz display. In some of the expanded displays two adjacent groups of signals are shown. Once an enlarged pattern is displayed, the line separations in Hz can be measured (remember that for a 500 MHz spectrum 1 ppm is 500 Hz). The middle signal at 3.2 ppm is the most complex, and overlap of some multiplet lines has occurred. The structure and signal assignments for this compound will be disclosed by clicking the " Show Solution " button.
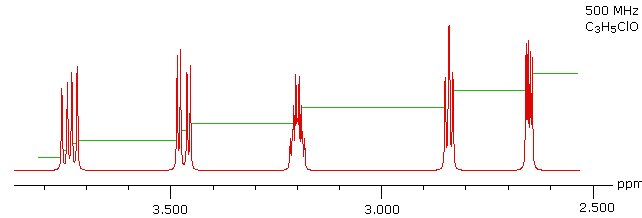
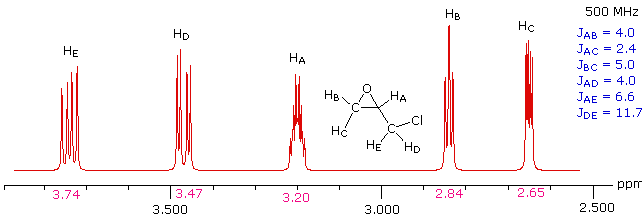
solution
This spectrum has several interesting features. First, hydrogens A, B & C are clearly different, and are spin-coupled to each other. Hydrogens B & C are geminally related, whereas A is oriented to B & C in a vicinal manner. Since JAB and JBC are similar, the HB signal is a broad triplet. Although hydrogens D & E might seem identical at first glance, they are diastereotopic, and should therefore have different chemical shifts. The DE geminal coupling constant is 11.7 Hz, so each of these hydrogens appears as a doublet of doublets.
The splitting of the HA signal is complex and not immediately obvious. The diagram on the right shows the consequences of the four operating coupling constants.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















