
Analysis of Molecular Formulas
 المؤلف:
William Reusch
المؤلف:
William Reusch
 المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
............
الجزء والصفحة:
............
 20-7-2018
20-7-2018
 2111
2111
Analysis of Molecular Formulas
Although structural formulas are essential to the unique description of organic compounds, it is interesting and instructive to evaluate the information that may be obtained from a molecular formula alone. Three useful rules may be listed:
1. The number of hydrogen atoms that can be bonded to a given number of carbon atoms is limited by the valence of carbon. For compounds of carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbons) the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be bonded to n carbons is 2n + 2 (n is an integer). In the case of methane, CH4, n=1 & 2n + 2 = 4. The origin of this formula is evident by considering a hydrocarbon made up of a chain of carbon atoms. Here the middle carbons will each have two hydrogens and the two end carbons have three hydrogens each. Thus, a six-carbon chain (n = 6) may be written H-(CH2)6-H, and the total hydrogen count is (2 x 6) + 2 = 14. The presence of oxygen (valence = 2) does not change this relationship, so the previously described C4H10O isomers follow the rule, n=4 & 2n + 2 = 10. Halogen atoms (valence = 1) should be counted equivalent to hydrogen, as illustrated by C3H5Cl3, n = 3 & 2n + 2 = 8 = (5 + 3). If nitrogen is present, each nitrogen atom (valence = 3) increases the maximum number of hydrogens by one.
|
Some Plausible
Molecular Formulas
|
C7H16O3, C9H18, C15H28O3, C6H16N2
|
|
Some Impossible
Molecular Formulas
|
C8H20O6, C23H50, C5H10Cl4, C4H12NO
|
2. For stable organic compounds the total number of odd-valenced atoms is even. Thus, when even-valenced atoms such as carbon and oxygen are bonded together in any number and in any manner, the number of remaining unoccupied bonding sites must be even. If these sites are occupied by univalent atoms such as H, F, Cl, etc. their total number will necessarily be even. Nitrogen is also an odd-valenced atom (3), and if it occupies a bonding site on carbon it adds two additional bonding sites, thus maintaining the even/odd parity.
|
Some Plausible
Molecular Formulas
|
C4H4Cl2, C5H9OBr, C5H11NO2, C12H18N2FCl
|
|
Some Impossible
Molecular Formulas
|
C5H9O2, C4H5ClBr, C6H11N2O, C10H18NCl2
|
3. The number of hydrogen atoms in stable compounds of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen reflects the number of double bonds and rings in their structural formulas. Consider a hydrocarbon with a molecular structure consisting of a simple chain of four carbon atoms, CH3CH2CH2CH3. The molecular formula is C4H10 (the maximum number of bonded hydrogens by the 2n + 2 rule). If the four carbon atoms form a ring, two hydrogens must be lost. Similarly, the introduction of a double bond entails the loss of two hydrogens, and a triple bond the loss of four hydrogens.
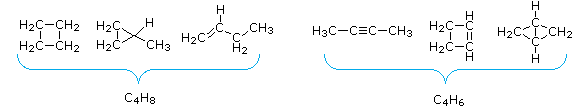
4. From the above discussion and examples it should be clear that the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon (CnHm) provides information about the number of rings and/or double bonds that must be present in its structural formula. By rule #2 m must be an even number, so if m < (2n + 2) the difference is also an even number that reflects any rings and double bonds. A triple bond is counted as two double bonds.
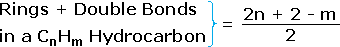
5. The presence of one or more nitrogen atoms or halogen substituents requires a modified analysis. The above formula may be extended to such compounds by a few simple principles:
- The presence of oxygen does not alter the relationship.
- All halogens present in the molecular formula must be replaced by hydrogen.
- Each nitrogen in the formula must be replaced by a CH moiety.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


