
Synthesis of clusters
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص567-568
الجزء والصفحة:
ص567-568
 2025-10-06
2025-10-06
 260
260
Synthesis of clusters
Key point: Three methods are commonly used to prepare metal clusters: thermal expulsion of CO from a metal carbonyl, the condensation of a carbonyl anion and a neutral organometallic complex, and the condensation of an organometallic complex with an unsaturated organometallic compound. One of the oldest methods for the synthesis of metal clusters is the thermal expulsion of CO from a metal carbonyl. The pyrolytic formation of metal cluster compounds can be viewed from the standpoint of electron count: a decrease in valence electrons around the metal resulting from loss of CO is compensated by the formation of MM bonds. One example is the synthesis of [Co4 (CO)12] by heating [Co2(CO)8]:
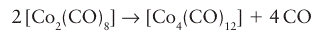
This reaction proceeds slowly at room temperature, so samples of octacarbonyldicobalt (0) are usually contaminated with dodecacarbonyltetracobalt (0). A widely used and more controllable reaction is based on the condensation of a carbonyl anion and a neutral organometallic complex:
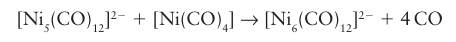
The Ni5 complex has a CVE of 76 whereas the Ni6 complex has a count of 86. The descriptive name redox condensation is often given to reactions of this type, which are very useful for the preparation of anionic metal carbonyl clusters. In this example, a trigonal-bipyramidal cluster containing Ni with formal oxidation number -2/5 and Ni(CO)4 containing Ni(0) is converted into an octahedral cluster having Ni with oxidation number -1/3. The [Ni5 (CO)12 ]2- cluster, which has four electrons in excess of the 72 expected for a trigonal bipyramid, illustrates a fairly common tendency for the Group 10 metal clusters to have an electron count in excess of that expected from the Wade-Mingos-Lauher rules. A third method, pioneered by F.G.A. Stone, is based on the condensation of an or ganometallic complex containing displaceable ligands with an unsaturated organometallic compound. The unsaturated complex may be a metal alkylidene, LnM=CR2, a metal alkylidyne, Ln MCR, or a compound with multiple metal-metal bonds:
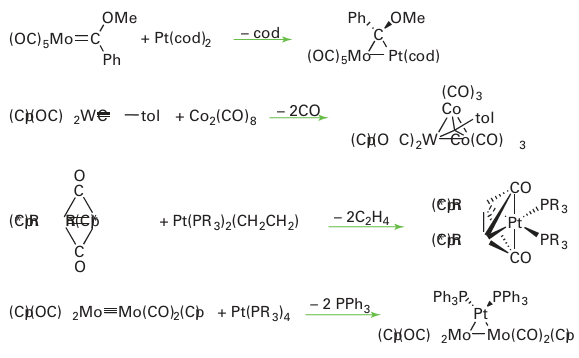
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


