

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Halides
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص408-409
2025-09-25
407
Halides
Key points: The halides of oxygen have limited stability but its heavier congeners form an extensive series of halogen compounds; typical formulas are EX2, EX4, and EX6. The oxidation number of O is -2 in all its compounds with thشe halogens other than F. Oxygen difluoride, OF2, is the highest

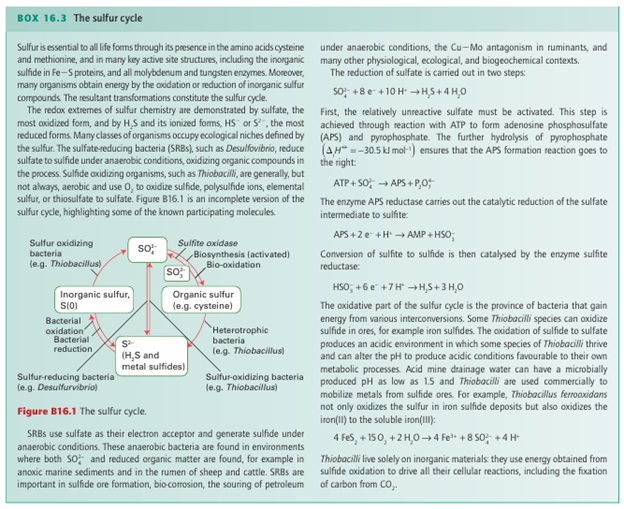
fluoride of oxygen and hence contains O in its highest oxidation state (+2). The structures of the sulfur halides S2F2 , SF4, SF6, and S2 F10 (Table 16.3) are all in line with the VSEPR model. Thus, SF4 has ten valence electrons around the S atom, two of which form a lone pair in an equatorial position of a trigonal bipyramid. We have already mentioned the theoretical evidence that the molecular orbitals bonding the F atoms to the central atom in SF6 primarily use the sulfur 4s and 4p orbitals, with the 3d orbitals playing a relatively unimportant role (Section 2.11a). The same seems to be true of SF4 and S2F10. Sulfur hexafluoride is a gas at room temperature. It is very un-reactive and its inertness stems from the suppression, presumably by steric protection of the central S atom, of thermodynamically favourable reactions, such as the hydrolysis
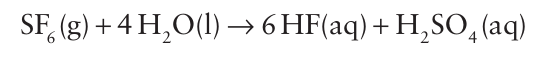
The less sterically crowded SeF6 molecule is easily hydrolysed and is generally more reactive than SF6 . Similarly, the sterically less hindered molecule SF4 is reactive and undergoes rapid partial hydrolysis:
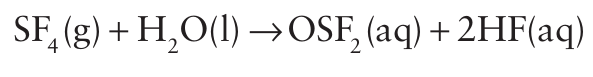
Both SF4 and SeF4 are selective fluorinating agents for the conversion of -COOH into CF3 and C=O and P=O groups into CF2 and PF2 groups:
Sulfur chlorides are commercially important. The reaction of molten S with Cl2 yields the foul-smelling and toxic substance disulfur dichloride, S2Cl2, which is a yellow liquid at room temperature (b.p. 138C). Disulfur dichloride and its fur ther chlorination product sulfur dichloride, SCl2, an unstable red liquid, are produced on a large scale for use in the vulcanization of rubber. In this process, S atom bridges are introduced between polymer chains so the rubber object can retain its shape.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















